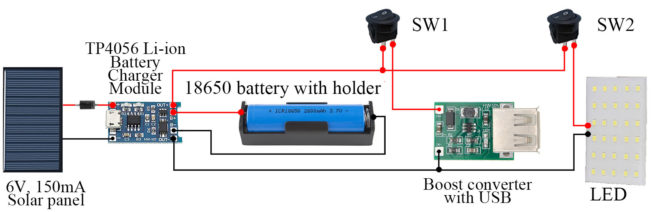
In this article, you will learn to design DIY Solar 18650 Charger as well as a solar emergency light. This device will help you charge a device through a USB port and it has an inbuilt led in it, which will serve as an emergency light when needed. Introduction of DIY Solar 18650 Charger with Emergency Light: Solar energy is the best way to reduce your energy consumption as it uses sunlight to produce energy. Sunlight can be utilized neatly, without harming our environment. So, here we are also going…
Read MoreDirect Digital Synthesis
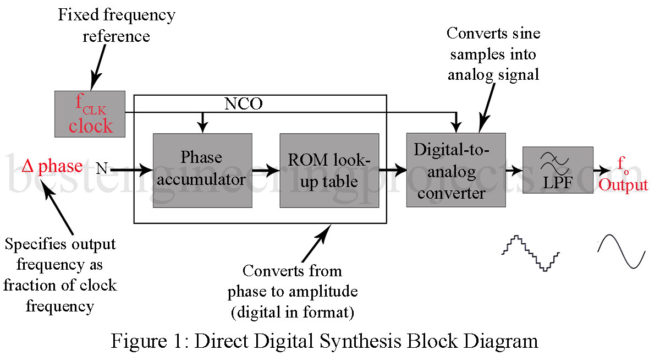
Direct Digital Synthesis Direct digital synthesis (DDS) systems became economically feasible in the late 1980s. They offer some advantages over analog synthesizers but generally tend to be somewhat more complex and expensive. They are, however, useful for some applications as will be discussed. The digital logic used can improve on the repeatability and drift problems of analog units that often require select-by-test components. These advantages also apply to digital filters that have replaced some standard analog ones in recent years. The disadvantages of DDS (and digital filters) are the relatively…
Read MoreArduino LiFePO4 Battery Charger Circuit
Amongst the rechargeable batteries available on the market, Lithium Iron Phosphate battery (LiFePO4 battery) or LFP battery (Lithium Ferro Phosphate) is widely used due to the various benefits offered, compared to other batteries. Longer life span, highly safe, lightweight, improved discharge, and charge efficiency are some of the advantages provided by the LiFePO4 batteries. In the market, you will find different types of LiFePO4 battery chargers that may or may not fulfill your requirements, and you may find them expensive. Previously, we had already discussed a DIY LiFePO4 battery charger…
Read MoreTemperature Compensated Arduino TDS Meter
In this article, you will learn about the effect of temperature on the TDS of water and finally, you will learn how to make a “Temperature Compensated Arduino TDS Meter”. TDS (Total Dissolved Solids) is the sum of organic and inorganic substances dissolved in water and, the methods used for the measurement of TDS value are Gravimetric Analysis and the Measurement of Electric Conductivity (EC). The gravimetric analysis provides reliable TDS value but it is time-consuming and is not very applicable when analyzing a lot of samples. So the measurement…
Read MoreTDS Sensor and Arduino Interfacing
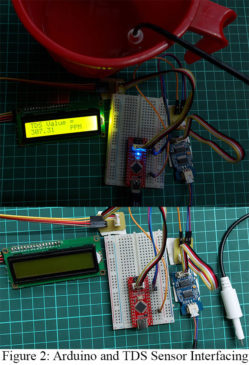
In this article, you will learn about TDS Sensor and Arduino Interfacing. TDS stands for Total Dissolved Solids and represents the amount of total dissolved solids (organic and inorganic substances) in water. TDS value is related to water quality. Typically, the higher the TDS value, the poorer the water quality. Pure water has a TDS value of 0, and the TDS value increases for increasing dissolved solids. But do remember that measuring the TDS value doesn’t provide you with the information on whether the dissolved solids are healthy for the…
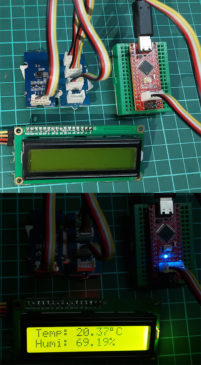
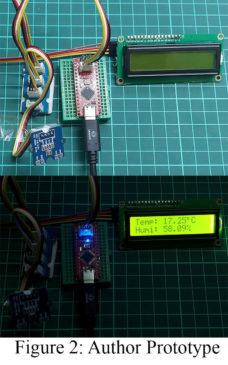
Read MoreInterfacing Temperature and Humidity Sensor TH02 with Arduino
TH02 is a consumer-grade digital temperature and humidity sensor. Although it can operate with a humidity range of 0-100% RH, it provides reliable or highly accurate data when the environmental conditions are between 0-70°C and 0-80% RH. The reason to use the TH02 sensor is that it provides a reliable reading in most home and daily applications if operated at its measuring range. It comes with its output calibrated in standard I2C format. In this article “Interfacing Temperature and Humidity Sensor TH02 with Arduino”, you will learn how to interface…
Read MoreInterfacing AHT20 with Arduino
AHT20 is a temperature and humidity sensor that utilizes a MEMS semiconductor capacitive humidity sensor and a standard on-chip temperature sensor. It has better performance and is more stable in harsh environments compared to DHT11, DHT22 which are commonly used temperature and humidity sensors. It has an astounding humidity measuring range of 0-100% RH with humidity accuracy as low as ±2% at 25℃. It comes in an SMD package and its output is calibrated in standard I2C format. In the article “Interfacing AHT20 with Arduino”, you will learn how to…
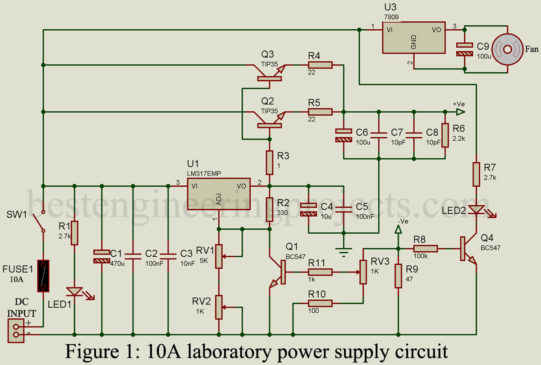
Read More10A Laboratory Power Supply Circuit
A good high-power laboratory power supply must-have device for electronic enthusiasm. As being electronic enthusiastic we all love to design our own bench power supply. So here in this article, you will learn to design your own variable current and voltage 10A laboratory power supply circuit. Features of 10A Laboratory Power Supply Circuit: Users can select voltage and current as per the requirement Constant current mode Short circuit indication and protection Voltmeter and ammeter Fuse for extra protection Applications It can be used as a general variable power supply. It…
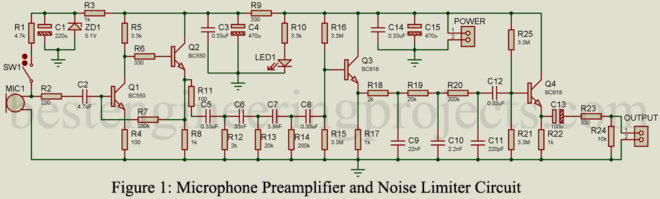
Read MoreMicrophone Preamplifier and Noise Limiter
The circuit posted here is of a microphone preamplifier and noise limiter. The main role of a microphone preamplifier circuit is to raise the signal level of the microphone output signal. A microphone is a transducer that converts sound signals to electrical signals. The output signal of the microphone is very small in a range of a few millivolts. This signal needs some level of amplification before the power amplification. Generally, the gain of the preamplifier is set to between 30 to 100. Besides pre-amplification, the circuit also limits noise.…
Read MoreFolded Dipole Antenna
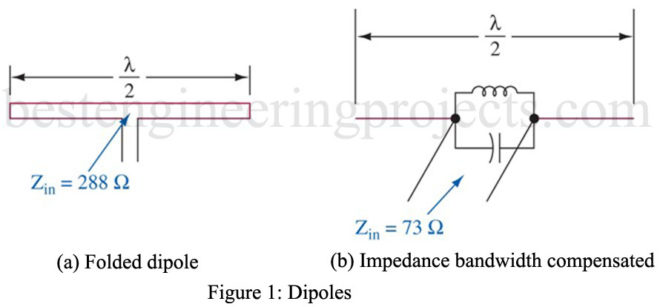
Folded Dipole Antenna: Recall that the standard half-wavelength dipole (Hertz antenna) has an input impedance of . Recall also that it becomes very inefficient whenever it is not used at the frequency for which its length equals (i.e., it has a narrow bandwidth). The folded dipole antenna is shown in Figure 1(a) offers the same radiation pattern as the standard Hertz antenna but has an input impedance of (approximately 4 x ) and offers relatively broadband operation. A standard Hertz antenna can provide the same broadband characteristics as the folded…
Read More