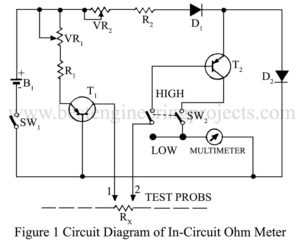
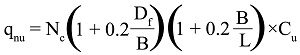While servicing gadgets, changes often occur when you feel the necessity of checking a defective resistor, shorted diode, transistor, or capacitor in a circuit. Didn’t you desire that all could have been done without switching on the gadget and without de-soldering and extracting the components? Here is a simple and effective remedy called In-circuit Ohm-meter. All you need in two transistors are a few resistors. Circuit description of In-circuit ohm-meter When an emf of about 1.5 volts is applied across the emitter-base junction of a germanium transistor, an emf of…
Read MoreMethod of Analysis for Mat Foundation
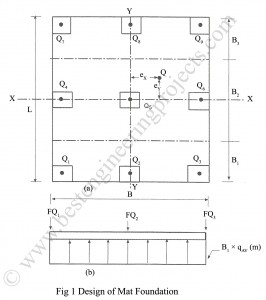
Method of Analysis for Mat Foundation The objective of the analysis for mat foundation is to find the bearing pressure underneath the mat. This depends upon the rigidity of the mat, rigidity of the superstructure and rigidity of the supporting soil. These factors make the determination of bearing pressure much complicated and necessitate some simplifying assumptions to be made. After the determination of bearing pressure, shear and moment are computed. Conventional Method | Method of Analysis for Mat Foundation The basic assumptions in conventional method are: Foundation is rigid relative to…
Read MoreAuto-off for Cassette Players
Most common stereo cassette players have an auto-stop deck mechanism but do not have the auto power-off function. The circuit is meant for cassette players having an operational voltage of 12 V DC with the facility of LED type VU meter. When the sound signal stops, the power is automatically switched off after a delay of approximately 30 seconds. Circuit Description of Auto-off Cassette players With sound present, the LEDs of VU meter emits light. The LDR on receiving light from LEDs gives a high pulse to transistor T1which charge…
Read MoreRaft Foundation Design
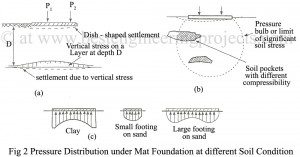
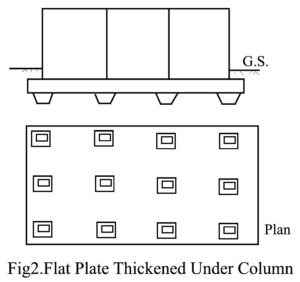
Raft Foundation Design General Considerations A mat supported on strong bedrock transmits the load in a relatively small area near columns. The pressure distribution on raft foundation will be as shown Fig. 1(a). If the mat rests on stiff or compact soils, the mat distributes the load to the subsoil in larger areas as shown in Fig. 1(b). If the mat rests on weak soil the pressure distribution on the mat tends to be uniform as shown in Fig. 1(c). In raft foundation design, the stresses developed underneath the mat…
Read MoreSettlement of Raft Foundation
The settlement is not a problem for raft on sands as allowable bearing capacity is computed on the basis of settlement criteria. However, settlement is of great concern when a raft rests on a deposit of normally consolidated clay. The net foundation pressure for computing settlement is taken as: ———– (1) The pressure in the Eq. (1) shall not cause settlement in excess of permissible value. If settlement exceeds the permissible limits, the foundation pressure should be reduced either by increasing the area under the structures or by increasing…
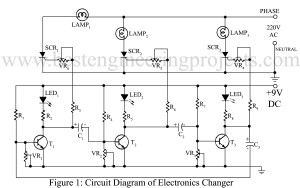
Read MoreRunning Light Circuit
In many situations, whenever a running light effect is required, a wooden wheel switch is needed. The wheel is driven by a motor which normally connects three switches, one by one producing a running light effects. Such a switching is very bulky and troublesome. Here is a simple electronic project “Running light circuit” with a very few components but which is equally effective. Circuit Description of Running Light Circuit In the circuit running light all transistors remain on except one which is off. This off sequence ‘travels’ through each transistor.…
Read MoreBearing Capacity of Mat Foundation
What is Bearing Capacity of Mat Foundation? Cohesionless Soil – In cohesionless soil a mat foundation does not fail in shear. For example, the bearing capacity of a raft foundation having a width of 6 m, and founded to a depth of 3 m in a sand deposit having relative density corresponding to SPT N-value of 10 is about 700 kN/m2 which is extremely high. In such case, the foundation may experience excessive settlement or even fail before attaining a bearing pressure of the order cited above. This means that the…
Read MoreMat Foundation | Types of Mat Foundation
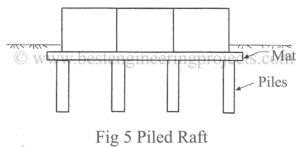
A mat foundation is a thick reinforced concrete slab supporting arrangements of columns or walls in a row or rows and transmitting the loads to the soil. It is used to support storage tanks, industrial equipment, silos, chimneys, and various tower structures. A mat foundation is used when the subsoil is weak and column loads are so heavy that the conventional spread footings cover more than 50 % of the building area. It is common to use mat foundation or deep basements to transfer the column loads to the underlying…
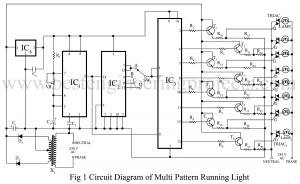
Read MoreMulti-Pattern Running Light Circuit
Running lights effect is not a new idea for electronics hobbyist. But this multi-pattern running light becomes unique as four patterns can be selected. In the first pattern, out of eight lights, alternate light go ‘on’ and ‘off’. In the second pattern, two adjacent lights go ‘on’ and the following two go ‘off’. This pattern is shifted from left to right. In the third pattern, four adjacent lights go ‘on’ and these are sifted to right. In the fourth pattern all the eights light go ‘on’ and ‘off’ one by…
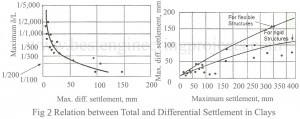
Read MoreRelation between Total and Differential Settlement
Based on actual observations on buildings Bjerrurn (1963) has provided some relationships between total and differential settlement for sands and clay. These are shown in Figs.1 and 2 for sands and clays respectively. It is revealed from the graphs that, in granular soils, the minimum differential settlement can be equal to the maximum permissible settlement. While in clays the differential settlement is much less than the maximum permissible settlement. In sands, the maximum differential settlement seldom exceeds 3/4 of the total settlement, while in clays it seldom exceeds 1/2 of…
Read More