In this article, we show 40+ different transmission line symbols used in transmission lines for various purposes. Transmission Line Introduction Transmission may take place via transmission lines, antennas, waveguides, or optical fibers. Sometimes a combination such as transmission line from the transmitter to its antenna, to receiving, to the transmission line, and to a receiver is used. A transmission line may be defined as the conductive connections between system elements that carry signal power. You may be thinking that if the wire connection between two points is a transmission line,…
Read MoreComparison of Transmission Systems
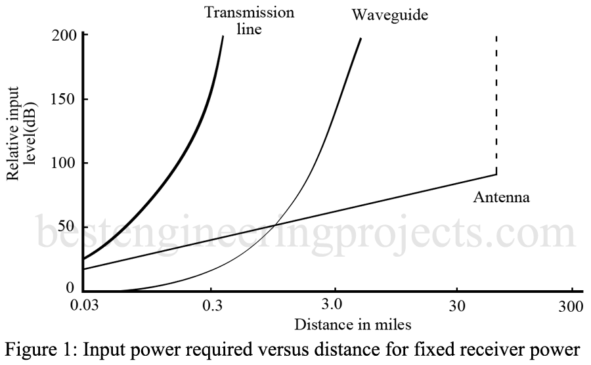
In the article “Comparison of Transmission Systems”, we will comparison transmission lines, waveguides, and antenna. The mode of energy transmission chosen for a given application would normally depend on the following factors: initial cost and long-term maintenance frequency band to be used and its information-carrying capacity selectivity or privacy offered reliability and noise characteristics the power level and efficiency. Naturally, anyone mode of energy transmission will have only some of the desirable features. It, therefore, becomes a matter of sound technical judgment to choose the mode of energy transmission best…
Read MoreDigital Power Supply Circuit
Most of us hear about the variable power supply, it is a power supply unit that provides almost all standard power supplies. How’s that if we combine a variable power supply and a digital control technology. Here, we have designed and verified a DC power supply circuit with the facility of digital control. The unit digital power supply circuit provides a variable, fluctuation-free and regulated ten different DC power supplies. These are 1.5V, 3V, 4.5V, 5V, 6V, 7.5V, 9V, 10.5V, 12V positive power supply, and 12V negative power supply. One…
Read MoreTraveling Wave Tube | Construction | Operation
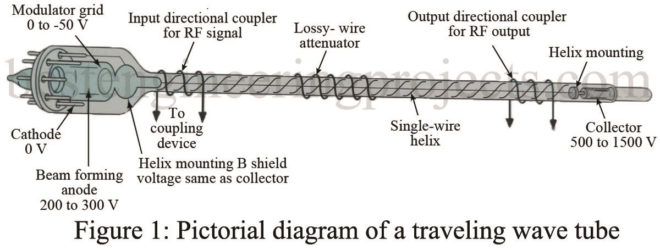
The traveling wave tube (TWT) is a high-gain, low-noise, wide-bandwidth microwave amplifier. Traveling Wave Tube are capable of gains of 40 dB or more, with bandwidths of over an octave. (A bandwidth of one octave is one in which the upper frequency is twice the lower frequency.) TWTs have been designed for frequencies as low as 300 MHz and as high as 150 GHz and continuous outputs to 5 kW. Their wide-bandwidth and low-noise characteristics make them ideal for use as RF and medium-power amplifiers in microwave and electronic countermeasure…
Read MoreMagnetron Operation | Magnetron
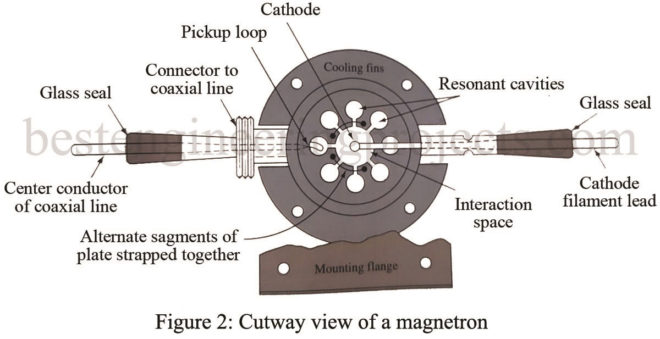
In this article, we will discuss Magnetron and basic Magnetron Operations. The magnetron is an oscillator unlike any other that. A magnetron is a self-contained unit. That is, it produces a microwave frequency output within its enclosure without the use of external components such as crystals, inductors, capacitors, etc. Check out the article on the Application of Microwave. Basically, the magnetron is a diode and has no grid. A magnetic field in the space between the plate (anode) and the cathode serves as a grid. The plate of a magnetron…
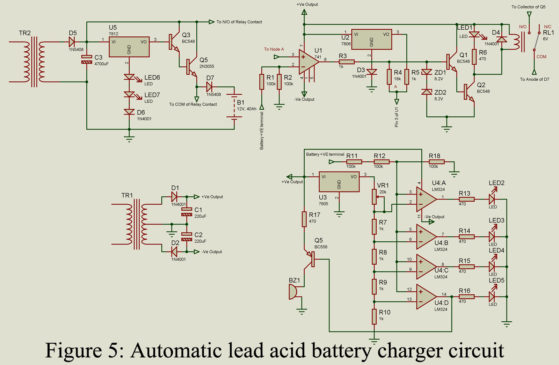
Read MoreAutomatic Lead Acid Battery Charger Circuit
An automatic lead acid battery charger circuit is designed to charge 12V, and 40Ah in different charging modes i.e. boost mode and float mode. This circuit can be used to charge large-capacity inverter batteries by replacing transformers and power transistors with higher ratings. To know the condition of the battery and charger unit, this circuit was incorporated with an audiovisual indication unit. Before going to the circuit description and working let’s see its salient features: Features of Automatic Lead Acid Battery Charger Circuit Automatic charger the battery and maintain the…
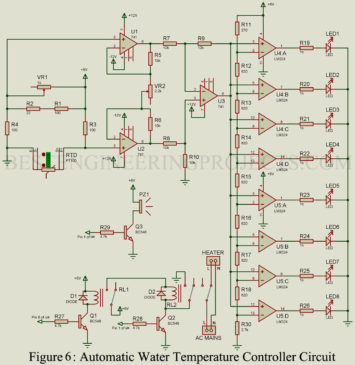
Read MoreWater Temperature Controller Circuit
The article posted here is of Water Temperature Controller Circuit based on PT100. For temperature indication, a LED bar graph designed using 8-LEDs is used. PT100 is a temperature transducer that produces changes in impedance whenever the temperature changes. It has definite resistance at each temperature within its temperature range because it is made from temperature-sensitive elements. The reasons for using platinum type temperature transducers are cheap, high stability, and wide operating temperature range i.e. -1800C to 800C. Check out the article on Resistance Type Thermometer PT100 is a probe…
Read MoreTroubleshoot Waveguide System
After completing this section, you should be able to troubleshoot the waveguide system. Waveguide problems are very similar to ordinary transmission line problems. The test equipment may look different, but it is doing the same things. A word of caution: Waveguide is commonly used to carry large amounts of microwave power. Microwaves are capable of burning skin and damaging eyesight. Never work on waveguide runs or antennas connected to a transmitter or radar until you are sure the system is off and cannot be turned on by another person. After…
Read MoreMicrowave Integrated Circuits
The field of communications now makes heavy use of the frequencies from 1 up to 300 GHz-we shall loosely refer to these as microwave frequencies. At microwave frequencies, even the shortest circuit connections must be carefully considered due to the extremely small wavelengths involved. The thin-film hybrid and monolithic integrated circuits used at microwave frequencies are called MICs (microwave integrated circuits). Check out the article on Applications of Microwaves Microwave Integrated Circuit Overview Obviously, the use of short chunks of coaxial transmission lines or waveguides is not practical for the…
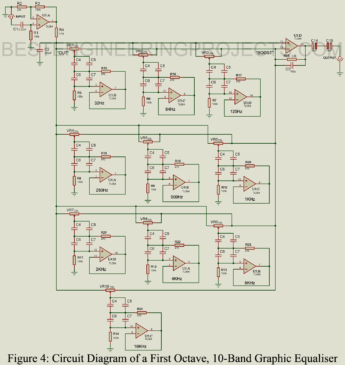
Read More10 Band Graphic Equalizer Circuit
This article is dedicated to those who want to make their high-quality low distortion 10 band graphic equalizer circuit. Before going to the circuit and it’s working let’s understand an equalizer and its types. An equalizer is simply a device that is attached to an instrument and with the help of this equalizer, we can set bass, middle, or treble. Sound or audio has a spectrum where frequencies are classified into different ranges. So, what are these bass, middle and treble? These are the range of frequencies, where the bass…
Read More