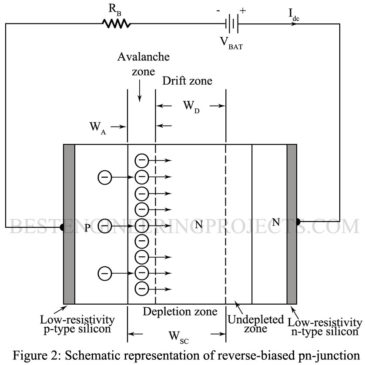
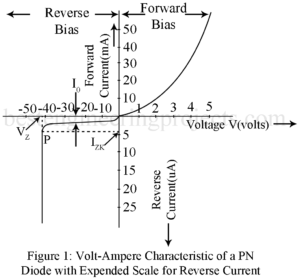
IMPATT Diode: IMPATT is an acronym for impact ionization avalanche transit time. The theory of this device was presented in 1958, and the first experiment diode was described in 1965. The basic structure of a silicon pn-junction IMPATT diode, from the semiconductor point of view, is identical to that of varactor diodes. The important difference between IMPATT and varactor diodes are in their modes of operation and in thermal design. Figure 1 shows a typical dc current versus voltage (I-V) characteristic for a pn-junction diode. In the forward-bias direction, the current increases rapidly…
Read MoreCategory: Electronic Tutorial
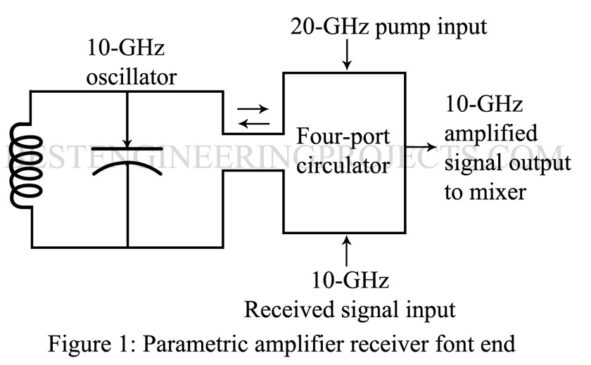
Parametric Amplifier
A parametric amplifier provides amplification via the variation of a reactance. This reactance is a parameter of a tuned circuit – thus the amplifier’s name. Consider a LC tank circuit that is oscillation at some microwave frequency. If the capacitor’s plates are pulled apart at the instant of time that the voltage across them is maximum positive, work has been accomplished. Since the capacitance, C, has been decreased and the charge, q, must remain the same, the voltage across the capacitor, V, must have been increased since V = q/C.…
Read MoreSquare Wave Generator using 741 IC
Op-amp 741 IC is one of the most popular and versatile operation amplifiers and can be used in a lot of applications including, comparators, wave generator amplifiers, etc. Today, we came up with another application of 741 IC i.e. Square Wave Generator using 741 IC. Objectives of Square Wave Generator using 741 IC: To design a square wave generator To describe the working of the square wave generator. Circuit diagram of the square wave generator The circuit of the square wave generator is shown in the figure below. One capacitor…
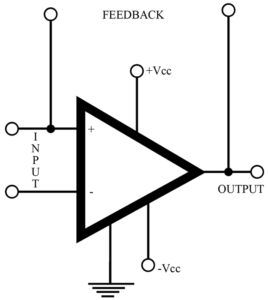
Read MoreKey Parameters of Operational Amplifier
In this article we will discuss about operational amplifier and key parameters of operational amplifier. So lets start with description. Description of operational amplifier: The basic op-amp is a DC coupled, high-gain, differential amplifier with external negative feedback. It is characterized by almost infinity open-loop gain, almost infinity input impedance, and almost zero output impedance. Invariably used with an external negative feedback element, the op amp provides a fixed gain, determined entirely by the ratio of the input resistance and the feedback resistance. As the feedback resistance increases, the gain…
Read MoreClass A Amplifier IC | Application and Parameters
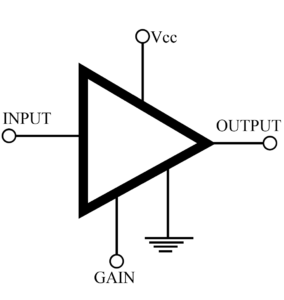
In Class A amplifier the input signal is reproduced, increased in amplitude, in exactly the same wave shapes at the output. To achieve this, the quiescent point (Q) is at the center of the collector current (IC) curve, so that the input signal as well as the amplitude output signal operates only over the linear portion of this curve. IC flows at all times. Class A amplifiers are used whenever the output wave shape must be the same, with a minimum of distortion, as the input signal. Operational amplifiers, and…
Read MoreDifferential Amplifier | Derivation | Key Parameters
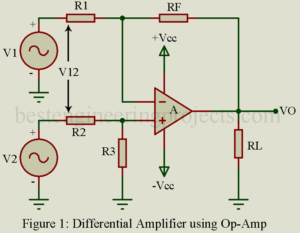
Differential amplifier have two input terminals that are both isolated from ground by the same impedance. This amplifier is basically used in industrial and instrumentation purpose because this type of amplifier are better able to reject common-mode (noise) voltage then single-input circuits such as inverting and non-inverting amplifier. Basically, a Class A voltage amplifier, the differential amplifier amplifies only the difference in voltage between its two terminals. Signals that appears at both terminals are not amplified, allowing the differential amplifier to pick up weak signals in the presence of strong…
Read MoreWhat are the Applications of microwaves
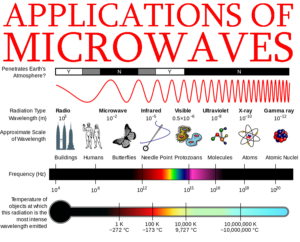
The are various applications of microwaves or we can say the application of microwaves can be broadly classified because of their use in various fields including cooking, long ranger communications, etc. The foundation of modern electronics and communications environment using radio frequency (RF) and microwaves were laid in the nineteenth century, named after Michael Faraday’s observations of magnetic field on light propagation in 1845, and James C Maxwell’s derivation of four basic equations of the electromagnetic theory of light. Because of the short physical wavelength of these frequencies, they present…
Read MoreZener Breakdown and Avalanche Breakdown
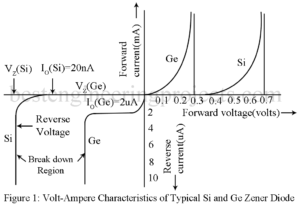
Figure 1 gives the volt-ampere characteristic of a PN diode including the breakdown region. Thus, when a PN diode is highly reverse biased, the junction may breakdown i.e. it presents extremely small resistance with the result that the current increases abruptly at an almost constant voltage. This current may be limited only by placing a suitable resistor in the external circuit. However, the breakdown is not permanent. The diode returns to its normal condition when this large reverse bias is removed. The breakdown of diode may be of two types:…
Read MoreTransition Capacitance and Diffusion Capacitance of Diode
Transition Capacitance CT of Diode (Space Charge Capacitance) With the increase of the magnitude of reverse bias, majority carriers move away from the junction i.e. the width W of the depletion layer increases. This uncovered immobile charge on the two sides of the junction constitute a capacitor of incremental capacitance CT is given by, ……..(1) Where dQ is the increase in the charge resulting from an increase dV in voltage. Hence, a voltage change dV in the time interval dt will result in a current i was given by,…
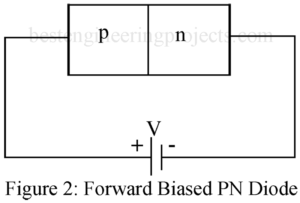
Read MoreVolt Ampere Characteristic of a PN Diode
What is Volt Ampere Characteristic of PN Diode? Current I in a PN diode in related to the junction voltage VV by the relation given by equation, ………..(1) Figure 1 gives the typical volt-ampere characteristic for a PN diode plotting above equation. With forward bias, the forward current remains essentially zero until the so called Cutin voltage VV of t diode is reached. This cutin voltage is defined as the voltage below which the forward current is less than 1% of the maximum rated current of the diode. This…
Read More