Entire project of proximity detector circuit is built with infrared transmitter, infrared receiver and 555 timer IC (such as using Seimens SFH50638 in TV sets). Proximity detector circuit, anyone can guess the operation performed by this circuit just with the name it is provided with. Infrared diode is the main soul of proximity detector circuit which is used in different equipment’s like burglar alarms, touch-free proximity switches for turning a light on, and solenoid controlled valves for operating a water tap.
Description of Proximity Detector Circuit Using 555 timer IC
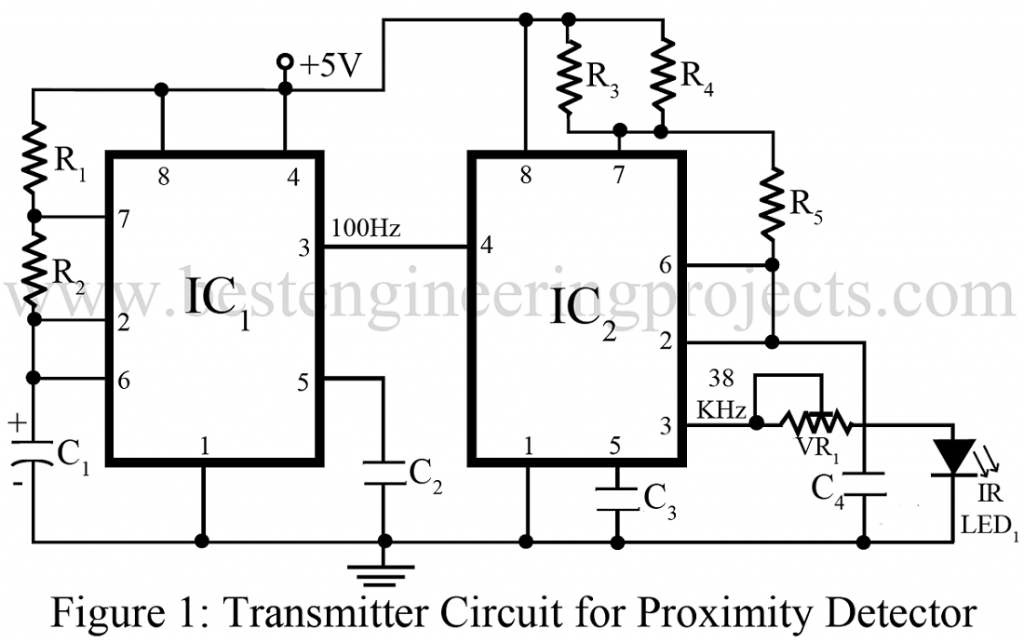
Transmitter Circuit | Proximity Detector Circuit Using 555 timer IC
As shown in the figure 1, two 555 timers (IC1 and IC2) wired in astable mode comprises the transmitter mode for proximity detector circuit. This part of circuit performs the work of driving an infrared LED; named as IR LED1 in the figure 1. The set up is setup such that transmission can be sensed by the infrared detector along with the circuit arrangement producing a burst output of 38 KHz, modulated at 100 Hz. In order to reduce the power consumption in the proximity detector circuit, the duty cycle of the 38 KHz astable multivibrator is maintained at 10 per cent.
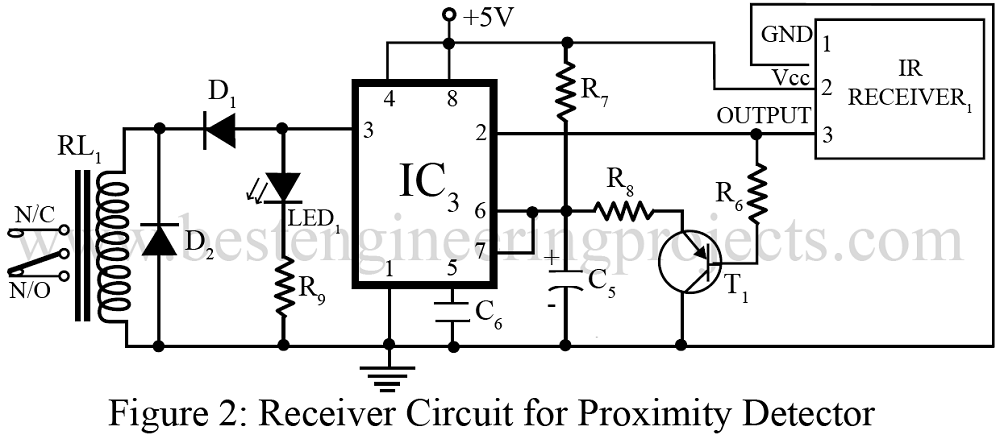
Receiver Circuit | Proximity Detector Circuit Using 555 timer IC
In similar way, an infrared detector circuit shown in figure 2 comprising IC 555 (IC3), wired in monostable mode, followed by pnp transistor T1 constitutes the receiving mode of the circuit. In this part of the circuit, as the infrared signal is received, the 555 timer in monostable mode is turned “on” and it persist in the same level as long as the reception of infrared signals continues.
When the receiving process comes to an end or no more signals are received, the IC3 goes off after a few seconds. The delay during this state depends on timing resistor capacitor combination of R7 – C5. In the particular circuit shown in figure 2, a 470 KΩ resistor and 47 µF capacitor offers a delay of 3 seconds. The capacitor used in this monostable mode is allowed to charge only when the reception of the signal has stopped unlike an ordinary mono stage. This difference is due to the presence of pnp transistor T1 in the proximity detector circuit that shorts the charging capacitor as long as the output from IR receiver module is available (active low).
The entire proximity detector circuit is used to detect proximity of an object present nearby. The circuit provides an extra benefit since both transmitter and receiver section of the circuit can be built on a single bread-board PCB. One must be careful enough to place the infrared receiver behind the infrared LED1 to avoid the consequence of infrared leakage.
Working of Proximity Detector Circuit using 555 Timer IC
The working of this circuit is so easy. The transmitting section produces infrared rays, an object moving nearby reflects these rays and the receiver section having a sensitivity angle of 60 ° sense the rays within this lobe. Due to which, the monostable IC3 is triggered.
Same principle can be used for turning the light “on” using a relay when a person comes in the vicinity and turns off as the person moves away. The sensitivity of the receiving section depends upon the current limiting resistor in series with the infrared LED1. Experimentally, we have found that with in-circuit if the resistance of preset VR1 is set at 20 Ω, the object at a distance of about 25 cm can be sensed. In addition to this, same circuit can also be used for burglar alarms based on beam interruption with additional advantage of housing both transmitter and receiving section in the same enclosure, reducing the cost and torture of circuit wiring.
Check out other Infrared (IR) based project posted in bestengineeringprojects.com
- Infrared Remote Controller Using Arduino
- Universal Arduino IR Receiver Circuit
- IR Remote Controller Fan Regulator using AT89C2051
- DIY Opto Reflector Sensor using 555
- Power Saver Circuit Diagram using PIR
PARTS LIST OF PROXIMITY DETECTOR CIRCUIT USING 555 TIMER IC
| Resistor (all ¼-watt, ± 5% Carbon) |
| R1, R9 = 1 KΩ
R2 – R4 = 5.6 KΩ R5 = 470 Ω R6 = 10 KΩ R7 = 470 KΩ R8 = 100 Ω VR1 = 100 Ω |
| Capacitors |
| C1 = 1 µF, 10V (Electrolytic Capacitor)
C2 – C4, C6 = 0.01 µF (Ceramic Disc) C5 = 4.7 µF, 10V (Electrolytic Capacitor) |
| Semiconductors |
| IC1 – IC3 = NE555 (Timer IC)
T1 = BC558 (General purpose, silicon PNP Transistor) D1, D2 = 1N4148 (Signal Diode) IR LED LED1 = any color LED IR Receiver = SFH-506-38 Siemens |
| Miscellaneous |
| RL1 = 5V, REED relay |