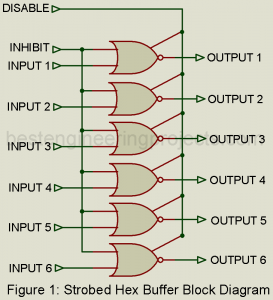
In this article, we will learn about strobed buffer or Inverter IC CD4502, its parameter, truth table and its application. Description of Strobed Buffer or Inverter IC This IC provides the basic buffer or inverter function as well as two additional control functions. As illustrated in figure 1, all six inputs are controlled by a single “inhibit” signal, and all six outputs are controlled by a single “disable” signal. This permits each of the six inputs and outputs to have a total of three possible states, as indicated by the…
Read MoreThree Phase AC Voltage Measurement using Arduino
Today, in this article, you will learn how to make Three Phase AC Voltage Measurements using Arduino. At first, we will show you how to measure single-phase AC voltage and then measure three-phase AC voltage. Features of Three Phase AC Voltage Measurement using Arduino: Can measure AC voltage of any amplitude. Show individual phase voltage. LED indication for individual phase voltage. For the protection of the control board (Arduino Board), a variable resistor is used i.e. output voltage must not be more than 4.5V even when Zener diode burnout. Working…
Read MoreBuffer or Inverter IC
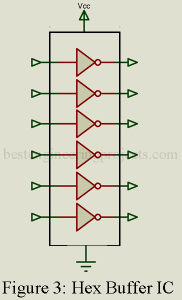
In this article we will discuss about buffer or inverter IC, its key parameters, internal circuit and applications. Description of Buffer or Inverter IC The buffer or inverter is one of the key functions used in all digital logic assemblies. As the name implies, this circuit provides a stage of buffering, separation in impedance, between other logic elements of buffering, separation in impedance, between other logic elements and, when it acts as inverter, changes the input signal into its complement. While buffer or inverters are most frequently used in combination…
Read MoreSinusoidal Frequency Meter using Arduino
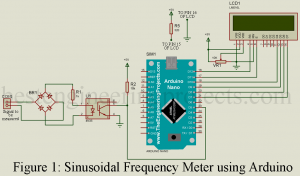
Today, in the article “Sinusoidal Frequency Meter using Arduino” you will learn how to measure the frequency of sinusoidal wave using arduino. With the purposed design one can measure sinusoidal frequency of about 20 Hz to 5KHz. Features of Sinusoidal Frequency Meter using Arduino Rectifier is used thus digital in natures. Optocoupler is used in order to isolate frequency circuit and control circuit and this optocoupler is also used to generate spike. Dedicated LCD for displaying frequency. Circuit Description of Sinusoidal Frequency Meter using Arduino Circuit of sinusoidal frequency meter…
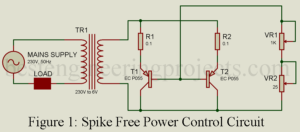
Read MoreSpikes Free Power Control
Here in this article, we will learn how to design spikes free power control circuits using a few electronics components like a transformer, transistor, etc. The commercially available lamp dimmers and other power control units create several problems associated with them. These incorporate SCR and diac-triac pairs, and the variation of power is achieved by varying the firing angle of these devices. This results in distorted waveform along with RF (radio frequency) spikes across the load. These RF spikes are received by frequency-sensitive instruments, TV, Radio, etc. Such interference with…
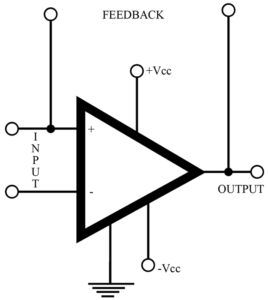
Read MoreKey Parameters of Operational Amplifier
In this article we will discuss about operational amplifier and key parameters of operational amplifier. So lets start with description. Description of operational amplifier: The basic op-amp is a DC coupled, high-gain, differential amplifier with external negative feedback. It is characterized by almost infinity open-loop gain, almost infinity input impedance, and almost zero output impedance. Invariably used with an external negative feedback element, the op amp provides a fixed gain, determined entirely by the ratio of the input resistance and the feedback resistance. As the feedback resistance increases, the gain…
Read MoreLinear Follower (Current) operational Amplifier
In the Article Linear Follower Amplifier we are going to discuss about current amplifier, its parameter, applications and comment. Current amplifiers are basically Class A Amplifier which usually have a voltage gain of 1 and effectively act as impedance transformers. Their main feature is their ability to develop a substantial output current. Sometimes they are called “linear followers,” similar to emitter follower transistor circuits. Current amplifiers are often used in series with an operational amplifier, inside the feedback loop, to provide additional output current. Key parameters of linear follower amplifier…
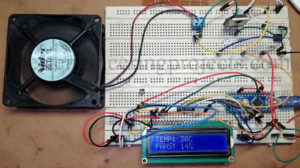
Read MoreArduino Based Temperature Controlled Fan
The project “Arduino Based Temperature Controlled Fan” is extended version of previous post “Temperature Controlled Fan using Arduino”. Speed of fan depends upon the temperature it detect. This project has various features like: Features of Arduino Based Temperature Controlled Fan Automatic fan speed control according to temperature. Temperature and speed are displayed over LCD. Control Circuit and Load circuit is isolated using opto-isolator 4N35 i.e. more protection. High Power drive circuit i.e. can drive high power high voltage DC fan. Maximum temperature indication using glowing LED. Circuit Description of Arduino…
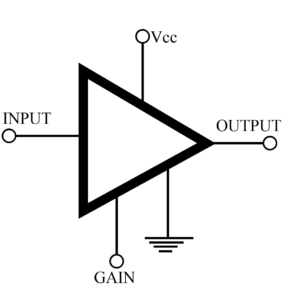
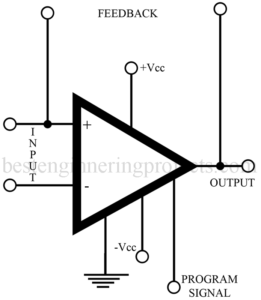
Read MoreProgrammable Operational Amplifier
In this article we will discuss about programmable operational amplifier IC, its key parameters, applications, parts number and comments. Programmable Operational Amplifier Description Some general-purpose op amps are available with an external tab that can be connected to a “set” or programmable current. This external terminal can control such important parameters as the power dissipation, bandwidth, slew rate, output current, input impedance, and input noise. While the programming current controls some of these parameters, other parameters will remain fixed. Externally supplied programming current can be in the form of a…
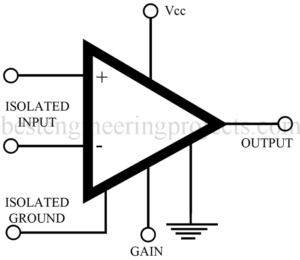
Read MoreIsolation Amplifier
In this article we will discuss about Isolation amplifier, its key parameters, applications and comments. So let’s start with description. Isolation Amplifier Description: Consisting of several stages of amplification, the input amplifier is either electrically or optically isolated from the output. The input amplifier is usually a differential amplifier, the output of which is RF modulated and then transferred through an RF transformer to the second stage, where it is demodulated and filtered. The DC power supply for the input amplifier section must also be isolated so that there is…
Read More