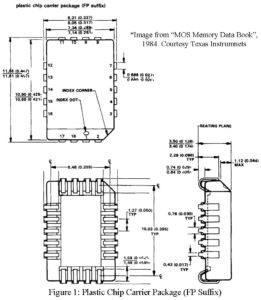
The demand for high-density, cost-effective printed circuit boards has promoted the electronic industry to seek alternative methods to traditional plated-through-hole technology. One such alternative is surface mounting, a technology traditionally used in hybrid fabrication. The advantage of surface mounting is numerous but the button line is that it is cost effective and will begin to displace plated-through-hole technology as the availability of surface-mount components increases. Texas Instruments is fully supporting the growth of the surface-mount industry with its line of plastic leaded chip carriers. An introduction to the surface-mount components…
Read MoreCategory: Electronics Design
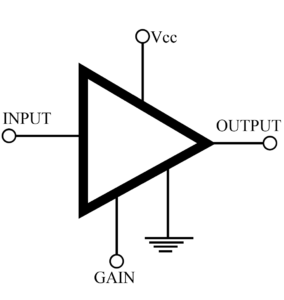
Class A Amplifier IC | Application and Parameters
In Class A amplifier the input signal is reproduced, increased in amplitude, in exactly the same wave shapes at the output. To achieve this, the quiescent point (Q) is at the center of the collector current (IC) curve, so that the input signal as well as the amplitude output signal operates only over the linear portion of this curve. IC flows at all times. Class A amplifiers are used whenever the output wave shape must be the same, with a minimum of distortion, as the input signal. Operational amplifiers, and…
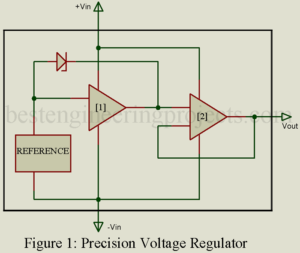
Read MorePrecision Voltage Regulator
There are various type of voltage regulator available in market, every single types of voltage regulator have it’s own advantage and applications. We have already discussed various type of voltage regulator like fixed voltage regulator, Adjustable voltage regulator, Tracking and floating voltage regulator. Here, in this article we are going to discuss about Precision voltage regulator and Switching voltage regulator. At first let’s see what is precision voltage regulator. Description of Precision Voltage Regulator High-precision voltage regulators are available for fixed output or adjustable output as well as for most…
Read MoreTracking and Floating Voltage Regulator
In this article we are going to learn what is tracking and floating voltage regulator with its key parameters, applications with appropriates comments. At first let’s see what about tracking voltage regulator. Description of tracking voltage regulator In effect, a tracking voltage regulator performs the function of two separate voltage regulators, positive and negative, with but a single adjustment to track both voltages accurately. As shown in figure 1, the voltage from either output to ground will remain the same regardless of load unbalance. Adjustment of the external potentiometer or…
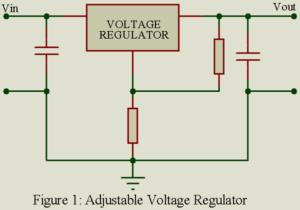
Read MoreAdjustable Output Voltage Regulator
The basic circuit of Adjustable Output Voltage Regulator is essentially the same as for fixed output voltage regulators, but there is provision for an external resistive divider or potentiometer to adjust the output voltage. Positive or negative polarity output voltage can be obtained by the same type of connections described in Fixed Output Voltage Regulator. Most of the adjustable type voltage regulators also contain one or more protective features such as over-voltage and over-temperature shutdown. Manufacturers data contain specific resistance values and/or potentiometer connections to provide the desired output voltage…
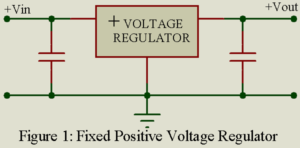
Read MoreFixed Output Voltage Regulator
This basic three-terminal device Fixed Output Voltage Regulator is available as either a positive or negative voltage regulator for a large range of fixed output voltages. In figure 1 small capacitor are shown at the input and output of the voltage regulator, because in many applications such capacitors are required to assure stable operation. Ordinarily we can obtain voltage regulators of the required polarity but it is also possible, as illustrated in figure 2, to use a negative voltage regulator to provide a regulated positive output voltage.Similar connection can be…
Read MoreVoltage Regulator Description and Application
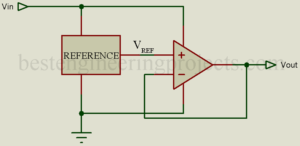
Voltage Regulator Description: IC Voltage regulators operates basically in the same manner as discrete circuit regulators. As illustrated in figure 1, the input voltage, usually the rectified ad filtered power-supply output, is applied to the reference circuit and to the op-amp. For optimum regulation, the op-amp must have high open-loop gain and a fairly large common-mode rejection ratio (CMMR). The reference source determines the accuracy of the regulated voltage output. Reference voltages can be provided by such simple device as a zener diode or by more complex multi-transistor circuits, such…
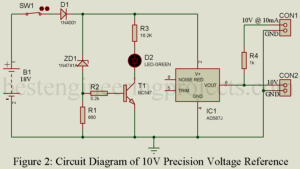
Read MorePrecision Voltage Reference Circuit
A precision voltage reference provides a constant, stable output voltage under a wide range of line, load, and temperature conditions. These devices usually work on the principle of bandgap voltage. Voltage drops are produced across two transistor base emitter diodes with unequal current flow. These voltage drops exhibit a negative temperature coefficient (the drop decreases as temperature is increased). However, the difference between the two voltage drops exhibits a positive temperature coefficient. When properly combined to equal a sum of 1.23V (the bandgap voltage), a near zero temperature coefficient is…
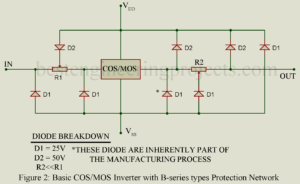
Read MoreGeneral Operation and Application Consideration for COS/MOS ICs
This article is intended as a guide to circuit and equipment designers in the operation and application of MOS integrated circuits. It covers general operating and handling considerations with respect to the following critical factors: Operating supply-voltage range Power dissipation and derating System noise considerations Power-source rules Gate-oxide protection networks Input signals and ratings Chip assembly and storage Device mounting Testing More specific information is then given on significant features, special design and application requirements, and standard ratings and electrical characteristics for COS/MOS A- and B- series logic circuits, and…
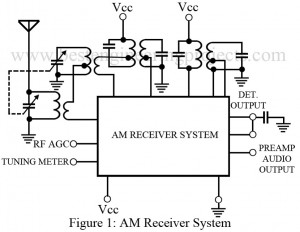
Read MoreAM Receiver System
A single IC as illustrated in the figure, consist of almost all the active components that an AM receiver constitutes in general cases. However the resonant networks required for the circuit operation, needed to be supplied externally. RF converter, IF amplifier, detector and AGC circuit, a built-in regulator zener diode, and the audio preamplifier stage are the crucial portion of the IC. We can also see in particular AM receiver system ICs, the RF amplifier is included and the tuning meter/ pre-amplifier is omitted completely from the system. Few parameters…
Read More