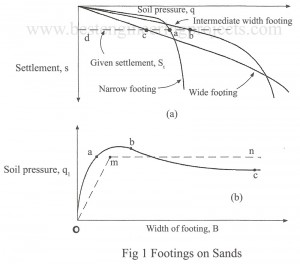
The computation of the bearing capacity from field plate load test has already been discussed in the chapter of site investigation. Here, the discussion will be limited to the estimation of bearing capacity from the results of standard penetration test. Cohesionless soil – In cohesionless soils, the bearing capacity is extremely high with respect to shear failure criteria. In sands, the shear failure criteria govern the capacity only in the case of very narrow footing located in loose sand below water table. In most of the cases the bearing capacity…
Read MoreCategory: Civil Projects
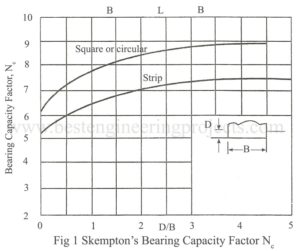
Skempton’s Theory for Cohesive Soil
Skempton 1951 suggested a bearing capacity theory for saturated clay for which ɸ = 0. Skempton gives Nc, the bearing capacity factor on the basis of theory, laboratory tests and field observations. It was found that the value of Nc increased with the increase in Df/B ratio. The expression for Nc proposed by Skempton is given below. For Strip footings, Nc = 5(1+0.2Df/B), with a maximum limiting value of 7.5 ———- (1) For square and circular footings, Nc = 6(1+0.2Df/B), with a maximum limiting value of 9.0 ———-…
Read MoreHansen’s Bearing Capacity Theory
Hansen 1970 proposed a general bearing capacity equation. This equation is widely used because the equation can be used for both shallow as well as deep foundation. Full scale test on footings has indicated that the Hansen equation gives better correlation than the Terzaghi’s equation. Terzaghi’s equation is known to give conservative results. However, it is still in wide use for its simplicity. The proposed form of the equation is: ———- (1) Table 1 Shape, Depth, load Inclination, Ground and Base Inclination factors. Use term with prime factor when Shape…
Read MoreInfluence of Water table on Bearing Capacity
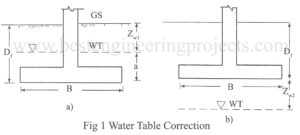
Terzaghi has developed the bearing capacity equation on the assumption that water table is at great depths. If water table is present close to the foundation, some modification is necessary. This is done as per the followings. Case 1 Water table above footing base The weight of soil below water table is reduced due to buoyancy. The influence of water table on bearing capacity is incorporated in the general bearing capacity equation with the help of Fig.1. Let, Zw1 = Depth of water table below ground level a = Height…
Read MoreFactor Affecting bearing capacity | Granular Soils | Cohesive Soils
What are the factor affecting bearing capacity? The bearing capacity of soil is influenced by various factors. The bearing capacity for cohesive and cohesionless soil is different. The physical features of foundation such as type of foundation, size of foundation, depth of foundation and shape of foundation significantly affect the bearing capacity. The amount of total and differential settlement is one of the main controlling factors for the bearing capacity of the soil. The relative density in the case of granular soil and consistency in the case of cohesive soil…
Read MoreTerzaghi’s Theory on Bearing Capacity Analysis
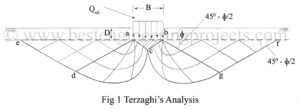
Terzaghi in 1943 gave a general bearing capacity theory for a strip foundation, called “Terzaghi’s Theory on Bearing Capacity Analysis“. For the first time, he developed his theory by incorporating the weight of the failure wedge in the analysis. Terzagi considered a continuous footing of width B placed at a depth of D below the ground surface as shown in fig.1. In the derivation of the equation, the following assumptions were made. The soil is homogeneous, isotropic and Columb’s law of shear strength is valid. The footing is continuous and…
Read MoreDevelopment of equation of Bearing Capacity by Prandtl
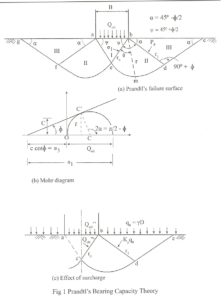
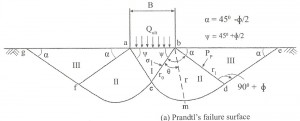
How to Development of equation of Bearing Capacity by Prandtl? equation of Bearing Capacity by Prandtl: As failure surfaces are symmetrical only forces acting on the right side of the wedges are considered. According to Prandtl, the bearing pressure Qult acting at the base ab of the footing is transmitted through the soil wedge abc on to the face bc, according to the Pascal’s law, pressure is undiminished and same in all direction. The state of stress within the wedge on the line bc may be explained with respect to…
Read MorePrandtl and Bell Theory on Bearing Capacity Analysis
Prandtl and Bell Theory on Bearing Capacity Analysis: Prandtl 1920 developed an equation based on his study of penetration of long hard metal puncher into softer materials for computing the ultimate bearing capacity. Assumptions made by Prandtl and Bell Theory on Bearing Capacity Analysis The material is softer, homogeneous and isotropic. The material is weightless and possesses only friction and cohesion. The problem is two dimensional The base of the puncher is smooth. The material behaves as a rigid body. The volume change will be Zero. The resulting deformation will…
Read MorePiled Foundation | Types of Pile
Piled Foundation: A pile is a slender structural member having very small area of cross-section relative to its length. It is a deep foundation where depth is greater than the width. It is used when shallow foundations cannot support the structure. Design Criteria of Piled Foundation A pile foundation must fulfill the following requirements: The material itself must not be over-stressed There must be an adequate factor of safety against a shear failure The settlements must be within the tolerable limits It should not over stress the underlying soft strata.…
Read MoreBearing Capacity Analysis | Pauker – Rankine Method
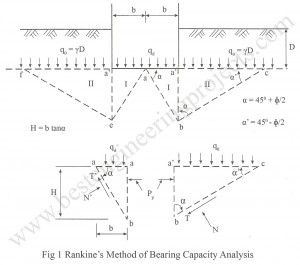
Bearing Capacity Analysis | Pauker – Rankine Method The methods suggested by Pauker Rankine Method are based on theory of classical earth pressure. This was postulated by Pauker a military engineer in 1850 and then modified by Bell in 1915. Pauker’s theory is only applicable to sands. Bell extended this theory for cohesive soils. Both the theories have not taken into account the width of the foundation. Since the equation has been developed based on Rankine’s earth pressure theory, the theory is called as Rankine’s theory for the determination of…
Read More