The pile spacing mainly controls the behavior of pile groups. The spacing should not be too small so that upheaval of ground surface takes place during driving into dense or in-compressible material. On the other hand, if spacing is too large, uneconomic pile cap may result. When driving piles in sand and gravels, it is advisable to start driving at the center of the group and then to work outward, in order to avoid difficulty with “tightening up” of the ground. In the group the following minimum spacing is recommended.…
Read MorePile Driving Formula | Engineering News Formula
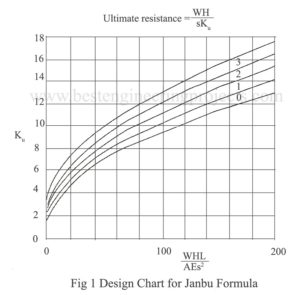
Many attempts have been made in the past to determine the relationship between the dynamic resistance of a pile during driving and static load carrying capacity of the pile. These relationships are called pile driving formula and have been established theoretically and empirically. Of many pile – driving formula, which have been, proposed Engineering News Formula, Hiley Formula and Janbu Formula are widely used. Among these the Hiley Formula and Janbu Formula are convenient to use and give reasonable predictions of ultimate bearing capacity of driven piles in granular soils.…
Read MorePile Capacity Based on SPT Results and Static Cone Penetration (CPT) Results
Pile Capacity Based on SPT Results On the basis of SPT results Meycrhof has suggested the following relationships for the ultimate capacity of piles. Displacement piles Qu = 400NAb + 2N’As ———- (1) H Piles Qu = 400NAb + N’As ———- (2) Bored Piles Qu = 133NAb + 0.67N’As ———- (3) Where, Qu = Ultimate total load in kN N = Average SPT value below pile tip N’= Average SPT value along the pile shaft As = Shaft surface area of pile in m2 Ab = Base area of…
Read MoreBored and Cast – In – Place Piles
The process of boring a hole for a pile seriously disturbs the clay in the neighborhood of the hole. Placing the concrete causes water to be absorbed by the clay surrounding the pile, leading to softening and reduced strength. The resistance of the pile is calculated by the relations: ———- (1) And ———- (2) Where w is 0.8 for B less than 1 m and 0.75 for B greater than 1 m. The Working load for the pile is given by: for plain shafts ————- (3) For…
Read MoreDriven Pile in Stiff Clay, soft Clay, Very Soft Clay
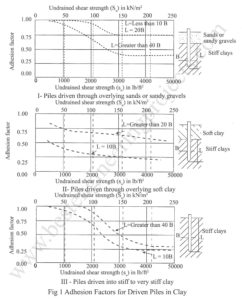
When piles are driven in cohesive soil, the shear strength is changed radically due to occurrence of following phenomena. Remolding Ground heave Formation of an enlarged hole Strain softening Remolding – Pile driving disturbs soil fabrics. This depends on sensitivity soils. With passage of time, the shear strength is regained due to the property called thixotropy. Soft sensitive soils regain their strength fully. After thirty days of driving about 75 % of strength is regained. Ground Heave – When a pile is driven in clay pore water pressure is developed…
Read MoreLoad Carrying Capacity Pile
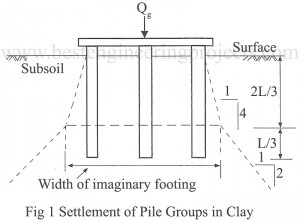
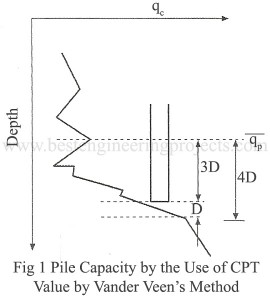
There are various methods of determining the load carrying capacity of single piles. They are: By Static Bearing Capacity Equations Based on SPT Results Based on CPT Results By Pile Driving Formula By Pile Loading Tests Static Bearing Capacity Equations The static methods give the ultimate bearing capacity of an individual pile, depending upon the characteristics of soil. Assume a pile of diameter D is driven to a length L from the ground surface as shown in Fig.1. Let Qu be the net load applied at the head of the…
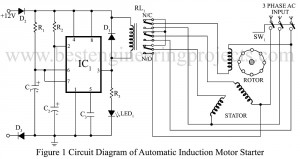
Read More3 Phase Induction Motor Starter
This circuit “3 Phase Induction Motor Starter” is one such starter. It is a very low-cost but highly reliable gadget, besides being fool-proof. Of all AC motors available, a polyphase induction motor is one that is mostly used in several kinds of industrial drives. this is because it is simple, extremely rugged, low cost, reliable, high efficient and requires little maintenance. Among the induction motors available, a squirrel cage machine is the best. However, such an induction motor can never be started by direct switching, as the motor can never…
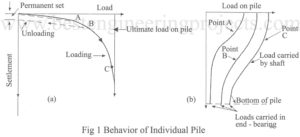
Read MoreBehavior of Single Pile and Pile Group Under loads
Behavior of Single pile Under Load Figure 1 shows a load settlement curve for a pile driven into a uniform soil. At early stages of loading the settlement is very small. The settlement at this stage is wholly elastic due to elastic deformation of pile and surrounding soil. When the pile is unloaded the deformation is almost wholly recovered as shown in Fig.1 (a). Strain gages attached along the pile shaft and base indicate that at small loads the pile shaft takes all the applied loads by friction developed between…
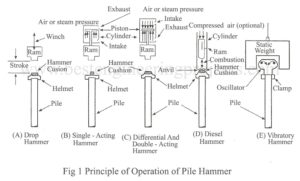
Read MorePiling Hammer | Types of piling hammer
Piles are driven into the ground by means of hammer. Piling Hammer are classified into following types as shown in Fig.1 Drop hammer Single acting hammer Double acting hammer Diesel hammer Vibratory hammer Drop hammer – A drop hammer is lifted up by rope and dropped freely on the pile head. During the driving operation, a cap is fixed to the top of the pile and a cushion is provided in between the pile and the cap. Single acting hammer – In a single acting hammer, a hammer is lifted…
Read MoreProportional Footing for Equal Settlement
Introduction to Proportional Footing for Equal Settlement To reduce the differential settlement due to live load variations for footings on grained soils, it is desirable to proportion all the footings in such a way that they have equal pressures under the service loads. Thus all footings would settle by equal amounts and the differential settlement would be considerably reduced. Steps on proportioning footing for equal settlement as suggested by Peck et al (1974) Determine dead load of footing. Determine the footing subjected to maximum live load. Compute the ratio of…
Read More