MOSFETs, or Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors, are widely used in many electronic applications because of their practical switching and amplifying functions. Two kinds of MOSFETs are used: the Enhancement MOSFET and the Depletion MOSFET. Each type differs in characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages. Here is a short overview to compare the pros and cons of enhancement and depletion MOSFETs to decide which will suit your application. Enhancement MOSFETs Starting from The enhancement, MOSFETs are the most applied type in today’s electronics. They are “normally off” when V_GS = 0, and thus, no…
Read MoreCategory: Field Effect Transistors
Common Drain Amplifier using FET
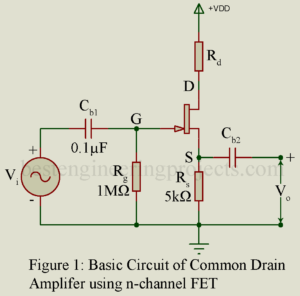
Common Drain Amplifier Introduction In the common drain amplifier, the input signal is applied between the gate and drain and the amplified output voltage is developed across a resistor in the source-to-drain circuit. The drain is the terminal common to the input and the output sides. Figure 1 gives the circuit of one stage of a common drain amplifier (CD) using n-channel FET. Rs is the load impedance placed in the source circuit. Quite often a resistor Rd is placed in the drain circuit to further stabilize the operation of…
Read MoreCommon Source Amplifier using FET
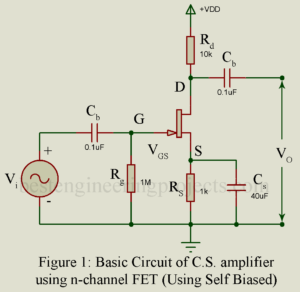
Common Source Amplifier In this amplifier, input signal is applied between gate and source and the amplified output voltage is developed across a load resistor in the drain circuit. Thus, source is the common terminal between the input side and the output side. Figure 1 gives the circuit of one stage of common source amplifier (CS) Amplifier using n-channel FET and with biasing arrangement. The typical component values are also shown in figure. This circuit is analogous to common emitter amplifier. On using p-channel FET, polarity of supply voltage is…
Read MoreMOSFET | Types of MOSFET | Circuit Symbol
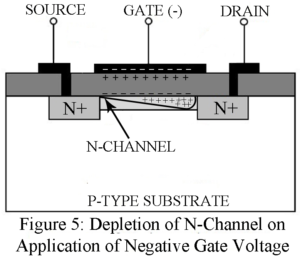
Metal Oxide Semiconductor FET (MOSFET) MOSFET is of greater commercial importance than the junction FET. Types of MOSFET Enhancement MOSFETs and Depletion MOSFETs. Enhancement Type MOSFET Figure 1 gives the cross-sectional view of a p-channel enhancement MOSFET. It consists of a lightly doped n-type substrate into which all diffused two highly dipped p + region spaced 10 to 20um apart. One region, say the left-hand region, acts as the source while the other region acts as the drain. A thin insulating layer of SiO2 of thickness 1000 to 2000 A…
Read More