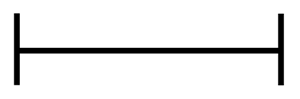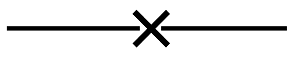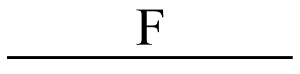In this article, we show 40+ different transmission line symbols used in transmission lines for various purposes.
Transmission Line Introduction
Transmission may take place via transmission lines, antennas, waveguides, or optical fibers. Sometimes a combination such as transmission line from the transmitter to its antenna, to receiving, to the transmission line, and to a receiver is used. A transmission line may be defined as the conductive connections between system elements that carry signal power. You may be thinking that if the wire connection between two points is a transmission line, why is it a whole transmission system? It turns out that at very high frequencies even simple wire connections start behaving in a peculiar fashion. What appears to be a short circuit may be no longer be one. Or, energy sent down the wire is reflected back.
Transmission Line Symbol
Figure 1:
Associated to future
Mechanical connection
Figure 2:
Conductive path
Major flow path
Wire
Figure 3: conductor
Figure 4: Delay
Figure 5: Dielectric path other than air for coaxial
Figure 6:
The direction of flow of information both ways simultaneously
The direction of flow of power both ways simultaneously,
The direction of flow of signal both ways simultaneously
Figure 7:
The direction of flow of information both ways simultaneously
The direction of flow of power both ways simultaneously
The direction of flow of signal both ways simultaneously
Figure 8:
The direction of flow of information either way but not simultaneously
The direction of flow of power either way but not simultaneously
The direction of flow of signal either way but not simultaneously
Figure 9:
The direction of flow of information either way but not simultaneously
The direction of flow of power either way but not simultaneously,
The direction of flow of signal either way but not simultaneously
Figure 10:
Electric shielding symbol
Magnetic shielding symbol
Figure 11: Isolated dc path in coax or waveguide
Figure 12: Mechanical connection with fulcrum symbol
Figure 12: Minor flow path
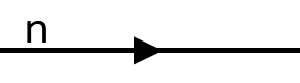
Figure 13:
One-way (to the right) flow of information where n is a waveform, frequency, or frequency range
One-way (to the right) flow of power where n is a waveform, frequency, or frequency range
One-way (to the right) flow of signal where n is a waveform, frequency, or frequency Range
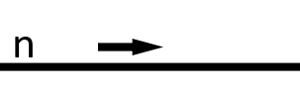
One-way (to the right) flow of information where n is a waveform, frequency, or frequency range
One-way (to the right) flow of power where n is a waveform, frequency, or frequency range
One-way (to the right) flow of signal where n is a waveform, frequency, or frequency Range
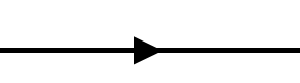
The one-way flow of information to the right
The one-way flow of power to the right
The one-way flow of signal to the right
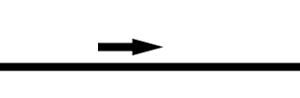
Figure 16:
The one-way flow of information to the right
The one-way flow of power to the right
The one-way flow of signal to the right
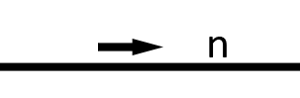
The one-way flow of information to the right, where n is a waveform, frequency, or frequency range
The one-way flow of power to the right, where n is a waveform, frequency, or frequency range
The one-way flow of signal to the right, where n is a waveform, frequency, or frequency range
Figure 18: Splice
Figure 19: Telephone line