In this Tutorial we are describing PN diode and types of PN Junction Diode.
What is PN Junction Diode?
A PN junction or P-N diode consists of a semiconductor having two regions, a p-region and n-region with a junction in between. The junction region or the transition region where the nature of the semiconductor material changes from p-type to n-type is usually very thin, typically 10-6 to 10-4 cm wide depending on the method of concentration.
What are the types of PN Junction Diode?
Depending on the method of construction, PN diodes may be classified as:
- Grown junction diode:
- Alloy type or fused junction diode:
- Diffused junction diode:
- Epitaxial planar diode:
You may also like Types of Transistor on the Method of Construction
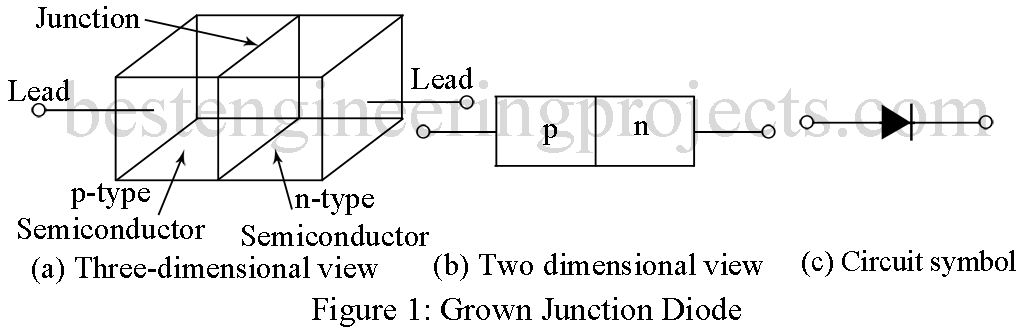
Grown Junction Diode | Types of PN Junction Diode:
Figure 1(a) and (b) show respectively three- and two-dimensional views of basic grown junction diode. Figure 1(c) gives the circuit symbol of a pn diode, common to all types. A grown junction diode is formed by first growing a semiconductor crystal of say n-type from extremely pure (impurities less than 1 in 109) molten Ge impurity (or Si) and little later changing the impurities from n-type to p-type by adding to the molten Ge impurities of p-type in large quantity.
Thus, a continuous crystal is formed which is partly p-type with a junction in between. This large crystal so formed is cut into a large number of small thin section each containing a p-region and an n-region with a junction in between. Each such section is polished and etched to remove surface impurity and then non-rectifying (ohmic) electrodes are deposited at each end of the bar. Finally, wires are soldered to these end electrodes. The whole assembly is then etched and covered with moisture proof grease, mounted in suitable mechanical structure and then hermetically sealed within a small glass envelope with leads passing through the foot. Opaque paint is usually coated on the outside of glass envelope to exclude incident light.
Alloy (or fused) Junction Diode | Types of PN Junction Diode
This is formed by placing a small dot or pellet of indium (trivalent) on a thin wafer of n-type Ge as shown in figure 2(a) and then baking this assembly for a short time at a high temperature of 5000C. This temperature is above the melting point of indium but below that of Ge. Then due to heating, the indium dot dissolves the Ge just below it and forms a-saturated solution. On cooling the saturated solution recrystallizes with sufficient indium content so as to change the impurities of the recrystallized region from n-type to p-type. Thus, this p-type Ge along with main n-type Ge of the wafer forms a pn junction. Connecting lead is attached to the indium pallet forming a non-rectifying contact. Further non-rectifying contact to the Ge wafer is made by welding to it a strip or loop of gold-plated wire. Figure 2(b) gives a section of the diode while 2(c) gives a three-dimensional view.
The whole assembly is then etched, covered with moisture proof grease, mounted in a suitable mechanical structure and hermetically sealed in a small glass envelope with leads passing through the foot. Opaque paint is then coated on the glass bulb to avoid incident light.
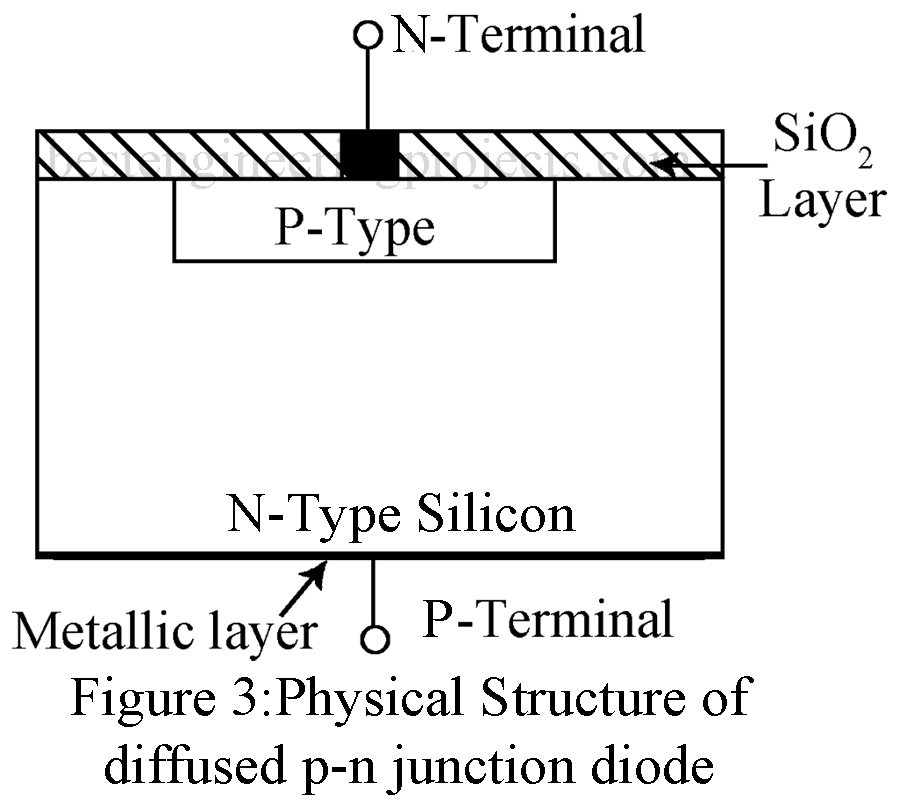
Diffused Junction Diode | Types of PN Junction Diode
A thin layer of SiO2 is thermally grown over the entire surface of a small (1.5mm x 1.5mm) Si wafer of thickness typically 0.3mm. This SiO2 layer is then photo-etched to form a mask and p-type diffusion is permitted through the opening in SiO2. For this diffusion purpose the Si wafer is placed in a furnace at 10000C in a gaseous atmosphere of high boron concentration. A sharp impurity concentration gradient results at the surface of the wafer and hence boron diffuses into the silicon wafer.
At this high temperature (10000C), several Si atoms move out of their lattice sites leaving vacancies for impurities atoms to move in. Again, a layer of SiO2 is thermally grown over the entire wafer, photo-etched and aluminum contact is made to the p-region. A metallic layer at the bottom of the wafer forms the n-electrode. Figure 3 shows the physical structure of diffused pn junction diode.
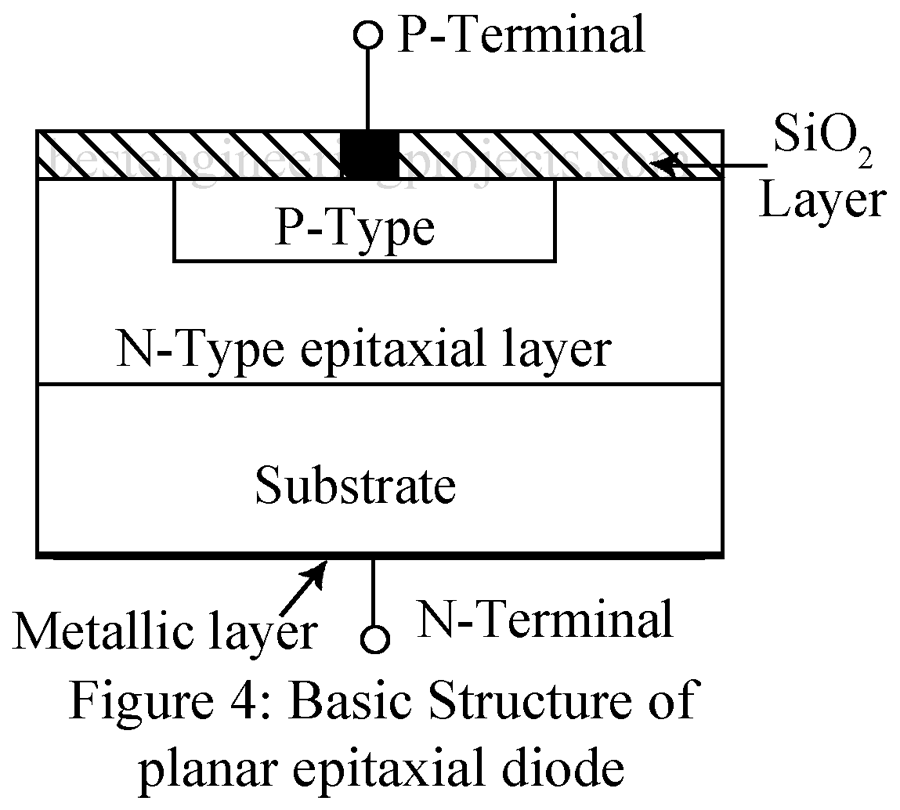
Epitaxial Planar Diode | Types of PN Junction Diode
Epitaxial growth means growth of a material upon a substrate (base) material such that the material so grown forms a continuation of the substrate crystal structure maintaining the same orientation. In an epitaxial planner device, a very thin (single crystal) high impurity layer of Si (or Ge) is grown on a heavily doped substrate of the same material. This complete structure then forms the n-region on which p-region is diffused.
Figure 4 shows the basic structure of epitaxial planar diode. SiO2 layer is thermally grown on the top surface, photo-etched and then aluminum contact is made to the p-region. A metallic layer at the bottom of the substrate forms the n-electrode to which lead is attached. This technique is popularly used in fabrication of IC chips.