What is Rotary Drilling or Open Hole Core Drilling?
During site investigation, drilling in rocks is very important step to produce continuous core. The strength, condition and sequence of the rocks, which will support the loading’s, must be set properly by appropriate examination and testing. These days, the loading’s are transmitted to the foundations. Different processes like construction of large dams, tunnels and presence of voids below a site often call for the drilling process through rocks. Out of other drilling processes, rotary drilling is undeniably the most expensive type of investigation since it requires different types of bits to suit multiple drilling conditions.
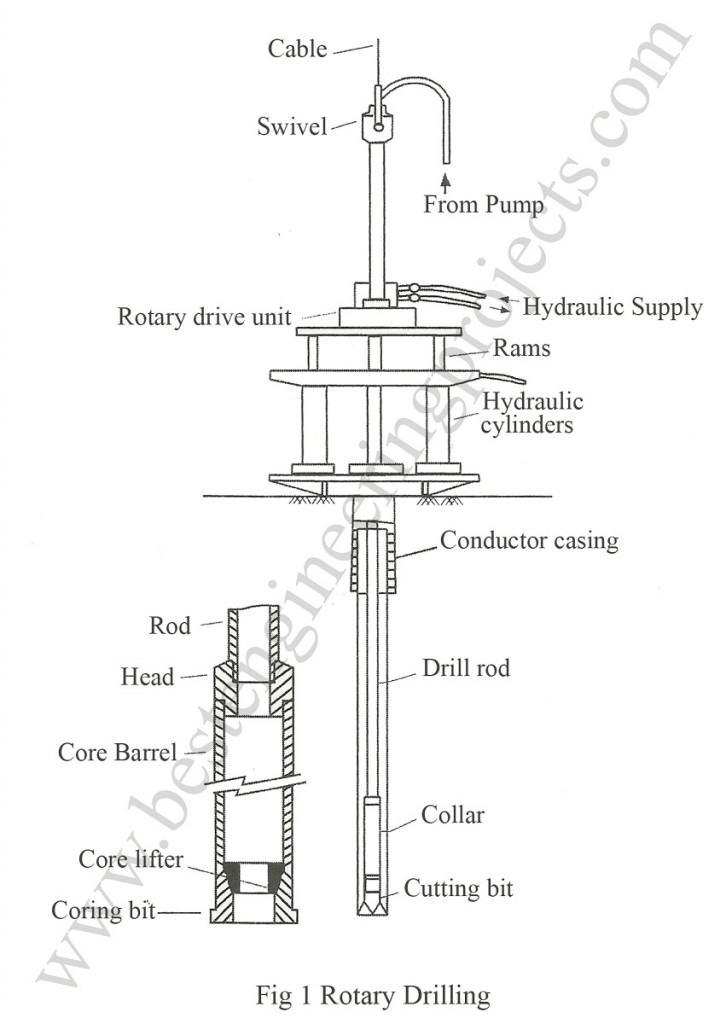
The driller executes the challenging part to choose the type of bit which will ensure the best core recovery in a particular formation in which he is drilling. Generally, bits used in rotary drilling are made up of diamond but in some cases, tungsten carbide bits are used, which are suitable for drilling through rocks.
The process of rotary drilling can be carried out in any direction. The rigs used come in wide range of sizes and are capable of drilling over 500 m. Similarly, the range of sizes of bore holes/rock cores are provided in the table 1 below. The bit is accompanied by a water pump, which is used to cool down the bit. Two forms of rotary drilling, namely, open hole and core drilling are in general use.
Open drilling is mostly suited in soils and weak rocks. Similarly, core drilling is used in hard rocks and hard clay’s. The bit of the rotary driller cuts an annular hole in the material and an intact core enters the core barrel. The core is frequently removed as a sample.
Core drilling has greater advantage over open drilling. This method is faster in comparison to other methods and the disturbance of sample inside the core barrel is negligible. However, this method is not suitable for deposits containing gravels and boulders because they rotate beneath the bit and do not break up the gravels and boulders.
Table 1 Sizes of Boreholes and Rock Cores
| Symbol | Diameter, mm | Symbol | Droll rod dia. mm | Symbol | Casing dia. mm | ||
| Hole | Core | Hole | Core | ||||
| EX, EM | 38 | 30 | E | 33 | EX | 46 | 38 |
| AX, AM | 50 | 30 | A | 41 | AX | 56 | 50 |
| BX, BM | 54 | 41 | B | 48 | BX | 73 | 54 |
| NX, NM | 75 | 68 | N | 60 | NX | 89 | 75 |