Accuracy and control are especially in great demand in the domain of test and measurement systems in today’s digital world. For that reason, there is much room for improvement in the design of the digitally controlled programmable attenuator circuit in terms of accuracy and flexibility of signal processing. The following article guides on how to design a programmable attenuator circuit with the OP07 operational amplifier and CD4052 analog multiplexer. Combining them yields a high degree of signal attenuation in a digitally controlled manner, quite essential in instrumentation and test or signal conditioning applications.
What is a Programmable Attenuator Circuit?
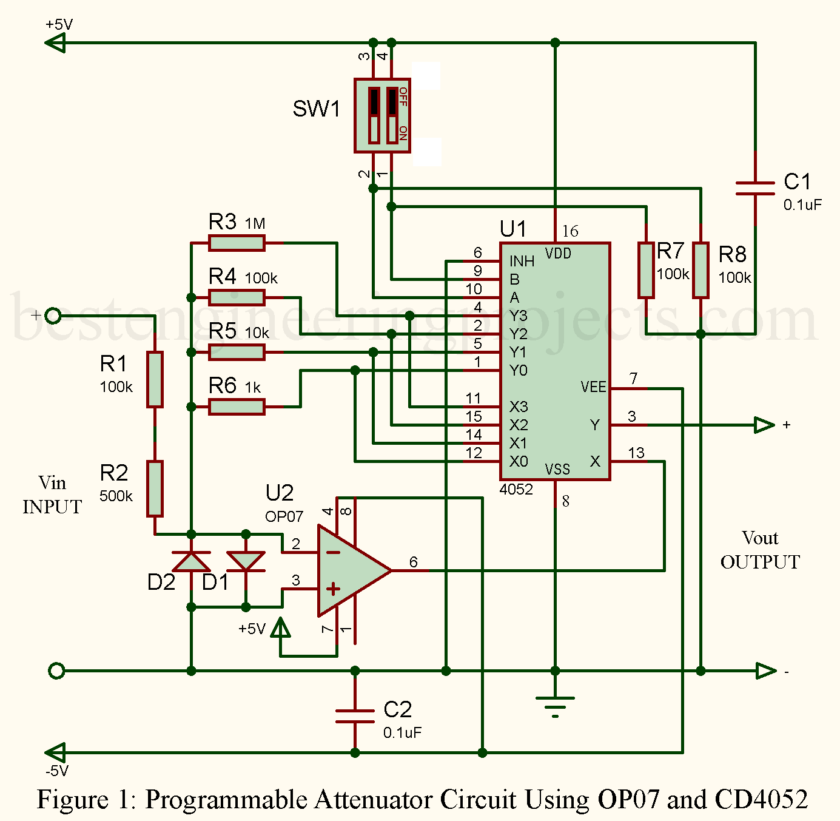
The programmable attenuator circuit is an analog circuit in which you are able to control the digital attenuation of the input signal. Usually, this kind of circuit is applied in the treatment of a signal by reducing the amplitude without warping its waveform. In this case, a digital system controls the attenuation level upon receiving commands from other sources, and therefore it will be suitable for automated systems, precision instrumentation, and remote measurement arrangements.
The existing circuit incorporating an OP07 op-amp and CD4052 analog switch can be combined in a very versatile and accurate way to achieve the attenuation of input signals with minimum error.
The Main Components of the Circuit
The major elements of the programmable attenuator circuit are:
- OP07 Operational Amplifier: These ultra-low offset voltage, low bias, current precision operational amplifiers feature high input impedance and are suitable for instrumentation and applications where a very high degree of accuracy is required.
- CD4052 Analog Multiplexer: The CD4052 basically is a dual 4-channel analog multiplexer, which enables the user to select different resistor networks and hence the attenuation factor of the circuit. The “on” resistance of the switch inside the CD4052 is bypassed to minimize errors in the output.
- Resistors and Diodes:
- Precision Resistors: The resistors used in this circuit are of 0.1% tolerance and 50 ppm (parts per million) to ensure minimal error during attenuation.
- Diodes (D1 and D2): Diodes are used for clamping the voltage across the op-amp to prevent excessive input voltage, protecting the sensitive components from damage.
Overview of a Circuit Diagram
The circuit consists of an OP07 operational amplifier with one configured-inverting amplifier, several resistors controlled by the CD4052 multiplexer to set the attenuation level. The digital control lines on the multiplexer select which resistor network is connected to thereby control the gain of the amplifier.
Basic Breakdown of Circuit: The circuit basically breaks down as follows:.
- Input Voltage: An applied input signal via a resistor network limits the current and reduces the signal to a non-destructive level.
- The multiplexer allows you to choose between different resistor paths using the logical values on control lines A and B, which can be adjusted either manually by throwing DIP switches or digitally through a microcontroller.
- OP07 Amplifier: The OP07 is an amplifier used in the inverting configuration and provides noise-free accurate stable amplification.
Truth Table for Control Input vs. Attenuation
Its attenuation level can be changed through the control inputs A and B of the CD4052 multiplexer. The truth table below shows the different attenuation factors:
| X,Y (ON-Switch Pair) | (2) B | (1) A | Gain (Attenuation) |
| X0, Y0 | 0 | 0 | 1/1000 |
| X1, Y1 | 0 | 1 | 1/100 |
| X2, Y2 | 1 | 0 | 1/10 |
| X3, Y3 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
The control inputs can be managed by a microcontroller, a decade counter, or manually through DIP switches, giving you complete flexibility over the attenuation settings.
How the Circuit Works
- The attenuation control: It selects one of several resistor values via the CD4052 multiplexer, which defines the gain of the inverting amplifier. In this scenario, selecting a particular resistor network applies a certain corresponding attenuation level to the input signal.
- Voltage Limiting: The diodes D1 and D2 work to clamp the input voltage to prevent excess voltage from reaching the op-amp. This becomes quite important in saving components from damage, especially when the extremes of the input signal are large.
- Inverting Amplifier Configuration: OP07 operational amplifier is in an inverting configuration – input signal is brought via a selected resistor, and the output is taken across the feedback resistor. Gain or attenuation of the amplifier depends on the ratio of the resistors and is controlled by the multiplexer.
Design Considerations
- Resistor Accuracy: To achieve a precise attenuation, the resistors must be of high accuracy. Using 0.1% tolerance resistors helps ensure that the attenuation is consistent and accurate.
- Voltage Rating: The input voltage must be limited to 500V maximum, and the resistors R1 and R2 are chosen to withstand this voltage while also limiting the input current.
- Digital Control Options: The control inputs for the CD4052 can be connected to a microcontroller I/O port, making it easy to automate the gain selection. Alternatively, you can use a DIP switch or thumbwheel switch for manual selection.
Applications of the Programmable Attenuator Circuit
- Test and Measurement Equipment: This is a very good circuit when one is performing automated test systems at which one requires different signal attenuation levels for calibration or measurement.
- Instrumentation: Precision instrumentation requires a digital treatment of signal levels so that one can have accurate data acquisition with no human intervention.
- Signal Conditioning: In applications where signals need to be conditioned before being processed by analog-to-digital converters (ADCs), this programmable attenuator can be used to ensure that the signal is within the required range.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building the Circuit
- Gather Components: You will need an OP07 op-amp, a CD4052 analog multiplexer, precision resistors (R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6), diodes (D1 and D2), and capacitors (C2, C3 for decoupling).
- Assemble the Circuit: Connect the resistors and diodes as shown in the circuit diagram, ensuring that the resistors used are of the correct tolerance for high accuracy.
- Configuring the Multiplexer: Wire the control inputs of the CD4052 into a microcontroller, or DIP switches so you can alter the attenuation factor.
- Power Up and Test: Apply power supply and an input signal; output levels to be verified with oscilloscope for different attenuations.
Safety Considerations
- High Voltage: This circuit is capable of handling an input voltage of up to 500V. Always be cautious when working with high voltages to avoid electric shock.
- Circuit Isolation: Note that this circuit does not isolate the input and output, so care must be taken when handling the input terminals.
Conclusion
Designing a programmable attenuator circuit using the OP07 and CD4052 allows you to achieve precise and flexible control over signal attenuation. This circuit offers the accuracy and digital control to give the finest results in the building of test equipment, instrumentation, or signal conditioning systems. An economical and powerful solution, the OP07 op-amp with the CD4052 multiplexer allows for ease in controlling signal levels.
The above steps will guide you on how to design and implement a programmable attenuator circuit. Feel free to ask any more questions or clarifications about it by reaching us through the comment section below.