Identity theft has always been a major security concern, even before the advent of the Internet. Now, social media sites, online banking, and even online gaming sites are ponds where identity thieves have ample fish to catch. So let’s talk about what is identity theft, what is a threat, and how to protect yourself from identity theft.
Your online identity consists of several unique details that ideally only you should know. While some people might think that your name, address, credit card information, and account number are the only bits of sensitive information that require protection, many other details can be used to steal your identity. Your IP address, usernames and password, PINs, account numbers, and even your secret questions for passwords can all be used in combination or individually for identity fraud.
A computer user working offline needs not to worry much about identity theft as long as his PC is protected with a descent login and password and he does not leave it unattended. Once you go online, however, you are vulnerable to various methods of attack. The biggest advantage for ID thieves online is that they do not have to physically steal your information or even steal information at all. More their details through malicious spam email, message, and website.
WHAT IS THE THREAT OF IDENTITY THEFT?
Any official or financial activity, transaction, or documentation requires a person to furnish identity proof. Whether you are purchasing a new SIM card for your phone, purchasing something with a credit card, booking a flight, or applying for a loan, none of these activities can be completed without ID proof, so it is obvious that you need to maintain the secrecy and legitimacy of your identity.
Should your details fall in the wrong hands, they can be used to open bank accounts, apply for loans, create email IDs and accounts on social media sites, or even purchase expensive items using your identity, leaving you with hefty credit card bills, thereby ruining your credit history and even affecting your reputation.
The hardest part about identity theft is that you will not be aware of it until you have noticed discrepancies in your bills or have been contacted about controversial or unacceptable material being posted by someone using your identity. Often, an intelligent attacker will know how to regulate these details to avoid detection.
HOW IT’S DONE
Your personal and confidential details can be stolen in many ways and sometimes not even directly from you, but rather from a service provider that has not taken sufficient security safeguards to protect its customers.
The simplest way for a fraudster to gather information from an unsuspecting user is to fool them into submitting the details themselves. Phishing emails are sent out to multiple email addresses requesting bank account information, passwords, PINs, or credit card details under the cover of a legitimate-looking website. This is a hit-or-miss process, where only a fraction of the recipients is fooled, but the attackers are nonetheless able to steal a considerable number of identities, which they can then use or distribute.
Trojans are also a very common cause of identity theft. Trojans are viruses that infect your system and then dispatch information saved on your PC such as login IDs and passwords or track keystrokes (known as keylogging) with which hackers can determine other personal details. Keylogging is a legitimate feature that many applications incorporate for functions such as parental control, hotkeys, and corporate security, Illegal keylogging software, however, can be designed to detect certain keystrokes when accessing specific sites such as your email, social media profiles, or secure banking sites, thereby recording your user ID and passwords.
Password strength is something that all sites stress upon, and for good reason. Cracking a long password containing different cases, characters and symbols take a lot longer than a password that is a common word or phrase. Another point often stressed is to have different passwords for different sites, so that a hacker cannot access all your accounts if he cracks the password for any one of them.
Users that do not heed these warnings often end up losing data and information from multiple profiles as hackers glean through their accounts and gather information. For example, skimming through an average user’s e-mail, Facebook, Twitter, and online bank account can provide a hacker with all required personal information, credit card, and financial details to apply for a new credit card or bank loan.
Another source of credit card information that hackers often target is payment gateways. Online shopping and bill payment has gained popularity all over the world over the last few years and now several services such as cell phone network providers, Internet services, e-shopping sites, etc. are beginning to offer online bill payment directly through their sites.
While most of these businesses are reliable and provide sufficient information to prove that your credit card information will be safe, some sites could have loopholes in their security measures or might fail to create a secure connection, in which case, attackers can easily access your credit card information and use it to make purchases online in your name.
thousands of subscribers’ personal and bank details.
A more recent form of identity theft, and one of the major concerns, is through social networking and social media sites. The danger with these services is that they are popular among youngsters, who are unaware of what type of information must not be shared online and how this information can be stolen to forge their identity.
Users with Facebook, Twitter, YouTube, Flickr, or any other such social media accounts often have weak privacy or security settings and also sometimes divulge too much information. Even something as simple as a status update or a video mentioning the names of your family members, pets or friends, birthdays, or even their whereabouts can be used to hack accounts and create duplicates or elicit data.
Identity fraud beginning with information collected from social media sites is often opportunistic where the attacker happens upon an account that lets strangers view all the information shared.
HOW TO PROTECT YOURSELF FROM IDENTITY THEFT
There are several preventive measures one can take to prevent their identity from being stolen. The general measures include monitoring your credit card bill and bank account statements regularly, divulging as little personal information as possible on social networking sites, identifying and avoiding phishing or spam mail or messages, and having effective antivirus software to prevent spyware and Trojans from infecting your machine
-
HAVE A STRONG AND UNIQUE PASSWORD
Any account, site, or service that requires a password does so for a reason, and in most cases, it is to prevent unauthorized users from gaining access to valuable information. It is important to have a strong password that is hard to crack so that hackers cannot get access to your data. Always use a mixture of upper- and lower-case alphabets, numbers, and symbols for your passwords, and make sure they are at least 8-10 characters in length. This makes it difficult for password cracking algorithms to determine your password.

Kaspersky website to make sure you have a strong password
You should also frequently change your passwords in case someone has hacked an account but hasn’t made any noticeable changes or transactions yet. It is also very important to have different usernames and passwords for different accounts so that a hacker that has successfully cracked one of your accounts cannot easily access other ones. Nowadays, most sites allow you to use your e-mail address as a username so it is also advisable to have multiple e-mail addresses on different clients for these purposes.
-
LEARN TO IDENTIFY PHISHING EMAILS
Attackers that use phishing mail to accumulate information create sites and web pages that mimic a service that you are already subscribing to and trust. A mail requesting password verification, personal details, or credit card information should be handled with caution. A legitimate business will rarely request such information via e-mail as they generally do so from secure, encrypted pages on their website. Always check the e-mail address of the sender to ensure that it is legitimate. A banking or financial institution or any other established online service will have an e-mail address associated with its domain name rather than a general e-mail service like Gmail, Hotmail, or Yahoo.
Also scan the mail itself for hints like the banner, disclaimer, copyright, and other fine prints and counter-check them with other mails or the website of the business or company. If you have any doubts or suspicions, contact the concerned company directly and verify if they have sent the mail and if it is secure and safe.
-
GET RELIABLE ANTIVIRUS SOFTWARE
Antivirus software can detect and warn you about phishing mail, spam, malicious websites as well as viral infection. While other measures can be taken to detect most of the aforementioned threats, viruses and worms cannot be stopped without a reliable antivirus program.
The most dangerous viruses to look out for are Trojans, which record keystrokes and collect data that can be used to mimic your identity. Trojans can spread through malicious sites, email attachments, corrupt software, or even files transferred from another device. Make sure you scan any downloaded content and external storage devices for malware before copying or running files.
Figure: Select Reliable Antivirus
-
LOOK FOR SECURE GATEWAYS
Whenever making an online payment or divulging personal information on a website, check for signs of a secure and encrypted service. A secure page uses an HTTPS connection, which provides encrypted communication and secure identification of a Web server.
Browsers also display a ‘lock’ icon, which indicates the site’s security policy and settings. Note that the lock icon must be displayed in your browser window and not on the page itself as many dubious sites use a bar at the bottom of the page to mimic the lock icon and fool users.
Figure: Secure Gateway
-
DON’T BE OVERLY SOCIAL ONLINE
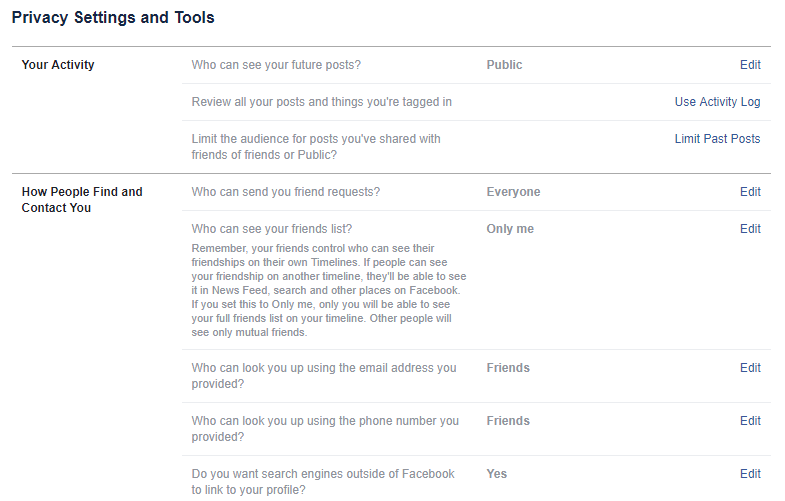
Revealing too much information online on your social networking accounts can come back to haunt you. Hackers and stalkers have been known to surf through Facebook and Myspace profiles to look for identity theft targets. Revealing your location, address, birth date, or other personal information on your social profile is best avoided unless you have the right security settings. Keep a check on the people you are adding as friends and make sure your security and privacy settings are set to prevent any unauthorized or unknown people from viewing your profile.
Figure: You can use Facebook’s feature to share certain information
only with a certain group of your Facebook friends.
Facebook and Twitter provide several different levels and options for privacy and security, so make sure you carefully go through all the settings to ensure your protection. Vulnerability on social media sites also comes in the form of apps. Always read and verify the type of information a quiz or poll or statistic app is gathering from your profile and check to see if it shares this data before you click “accept’.
-
NOT ALL FUN AND GAMES
Similar to apps on social networks, online games, including games on Facebook, are frequent targets for extracting credit card information. What used to be games to while away time, have progressed into complex games where you can use real-world money to purchase virtual money, online credits, in-game items, and expansions. These games often lack adequate security measures and are accessed by hackers to get credit card information.
There have been cases in the past where youngsters playing games on Facebook have given away credit card information, which has been used to forge their identities and apply for bank loans. In one case, the hackers even placed an initial payment on a car purchase.
-
CAN YOU TRUST THE PROVIDER?
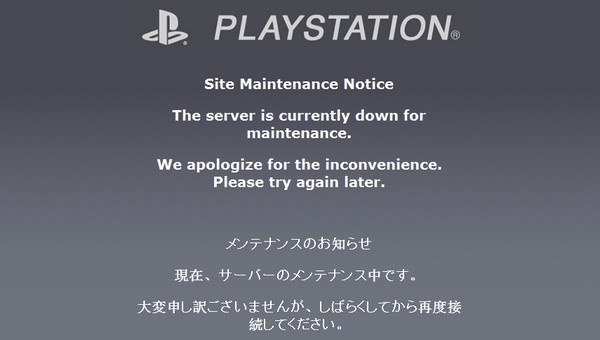
There have been numerous cases in the past of reputable, reliable service providers being caught out, having holes in their system that leak out their customer’s information. Multiple phone apps have been found to leak phone numbers and phone contacts, such as the recent Skype app for Android. Facebook has come under scrutiny on multiple occasions when users have questioned their privacy policies and security settings. The recent PSN debacle, where Sony’s PlayStation Network was hacked into and users’ credit card information was stolen also brings to light the number of threats your sensitive information faces.