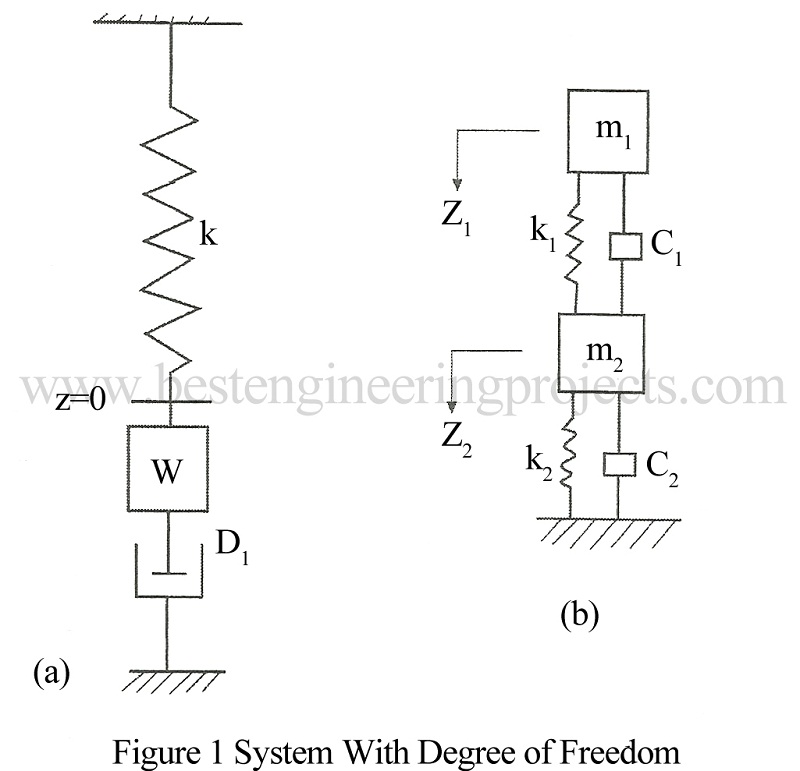
What is degree of freedom?
The Degree of freedom is defined as the number of independent coordinates which describe the motion of a system.
Figure 1 (a) shows a system with one degree of freedom while, Fig.1 (b) shows a system with two degree of freedom. A foundation block as shown in Fig.2 has six degree of freedom. The block can undergo into six independent displacements. We can have translation in X, Y, and Z directions and also rotation in X, Y and Z directions.
Loads on Machine Foundation
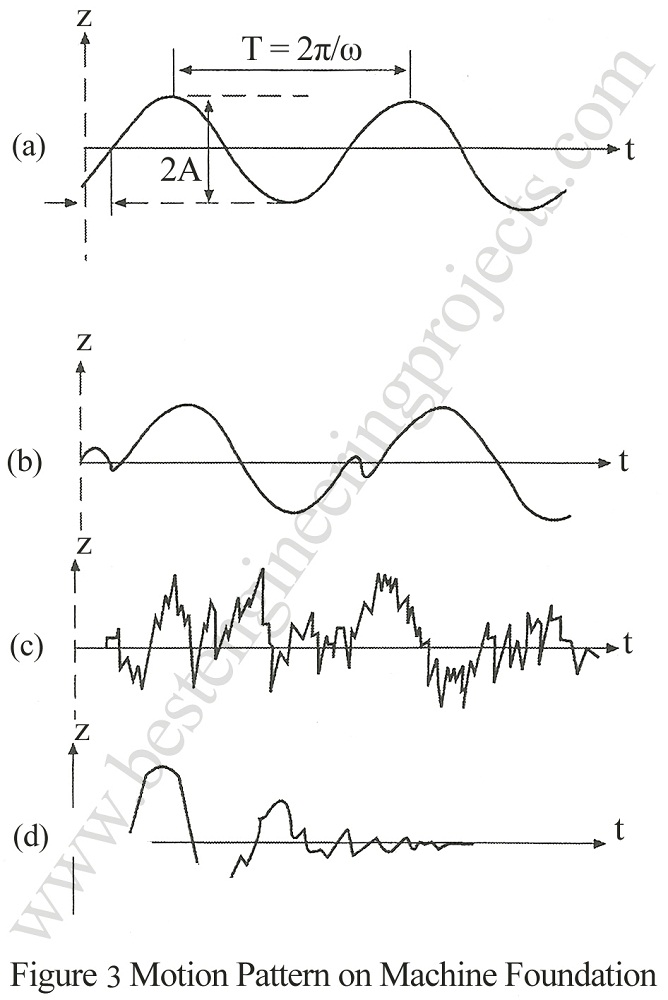
The loads transmitted by machine foundations comprise both static and dynamic loads. The static loads are weight of machine and foundation. The dynamic loads are repeated loads applied over a very long period of time but the magnitude is small. In vertical vibration a rigid foundation block may undergo four patterns of motion. This is illustrated in Fig.3
Figure 3(a) is a harmonic motion which a rigid block may follow in one dimensional vibration. Such motion is represented by a sinusoidal curve and is developed by a sinusoidal input force. Fig.3 (b) represents a periodic motion where the pattern repeats itself, but the motion is not a harmonic motion. This type of motion is developed by foundation supporting machinery which develops forces at two or more different frequencies. Fig.3(c) represents random motions developed by wind, waves and earthquakes. These forces have random input. Finally, Fig. 3(d) represents a transient motion resulted by short term application of forces or a pulsating loading.
Check out other article on machine foundation posted on bestengineeringprojects.com
- Types of Machines | Types of Machine Foundation
- Machine Foundation | Introduction and Description
- Design Criteria of Machine Foundation
- Method of Analysis of Machine Foundation