Before talking about various types of antenna symbols I would like to describe about antennas. Antennas for use at microwave frequencies. Antennas serve either or both of the following two functions: the generation and the collection of electromagnetic energy. In the transmission system, a radio-frequency signal is developed, amplified, modulated, and applied to the antenna. The RF current flowing through the antenna produces electromagnetic waves that radiate into the atmosphere. In a receiving system, electromagnetic waves “cutting” through the antenna induce alternating currents for use by the receiver.
To have adequate signal strength at the receiver, either the power transmitted must be extremely high or the efficiency of the transmitting and receiving antennas must be high because of the high losses in wave travel between the transmitter and the receiver.
Any receiving antenna transfers energy from the atmosphere to its terminals with the same efficiency with which it transfers energy from the transmitter into the atmosphere. This property of interchangeability for transmitting and receiving operations is known as antenna reciprocity. Antenna reciprocity occurs because antenna characteristics are essentially the same regardless of whether an antenna is sending or receiving electromagnetic energy.
Because of reciprocity, we will generally treat antennas from the viewpoint of the transmitting antenna, with the understanding that the same principles apply equally well when the antenna is used for receiving electromagnetic energy.
Antennas produce or collect electromagnetic energy and they should do so in an efficient manner. Consequently, antennas are composed of conductors arranged to permit efficient operation. The efficient operation also requires that the receiving antenna is of the same polarization as the transmitting antenna. Polarization is the direction of the electric field and is, therefore, the same as the antenna’s physical configuration. Thus, a vertical antenna will transmit a vertically polarized wave. The received signal is theoretically zero if a vertical E field cuts through a horizontal receiving antenna.
The received signal strength of an antenna is usually described in terms of the electric field strength. If a received signal induces a signal in an antenna 2 m long, the field strength is
or
. The received field strength is inversely proportional to the distance from the transmitter.
The list of various antenna symbols is shown below:
ANTENNA SYMBOL |
NAME OF ANTENNA |
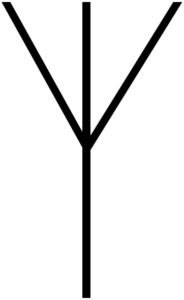 |
Antenna:
Antenna produces or collects electromagnetic energy and they should do so in an efficient manner. Consequently, antennas are composed of conductors arranged so as to permit efficient operation. The efficient operation also requires that the receiving antenna is of the same polarization as the transmitting antenna. |
 |
Turnstile Antenna:
Turnstile antenna is also called crossed dipole antenna, designed using two identical dipole antenna placed at the right angle to each other. The two current is applied to phase quadrature which is 900 out of phase. |
 |
Circularly Polarized Antenna:
The circularly polarized antenna is an antenna that is designed for producing or responding to circularly or elliptically polarized waves only. This type of antenna provides a high-gain omnidirectional circularly polarized radiation pattern. |
 |
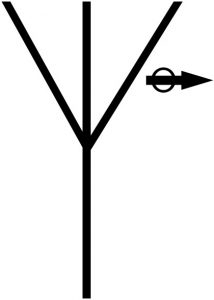
Adjustable Elevation
Radiation Antenna |
 |
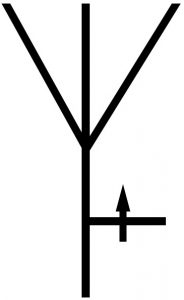
Adjustable Azimuth
Radiation Antenna |
 |
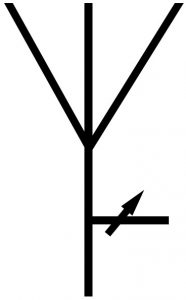
Fixed Azimuth
Radiation Antenna |
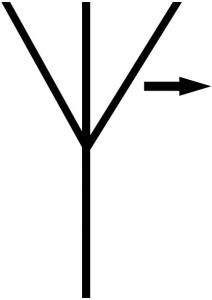 |
Horizontally Polarized
Antenna |
 |
Vertically Polarized
Antenna |
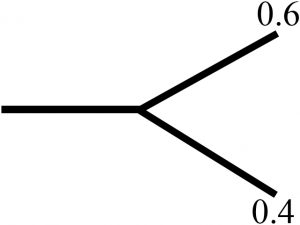 |
UHF or VHF Power
Divider |
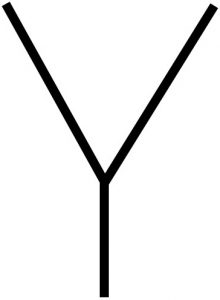
|
Horn Antenna
or Feed |
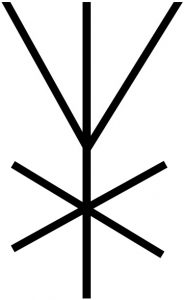
|
Direction Finding
Antenna |

|
Dipole Antenna |

|
Loop Antenna |
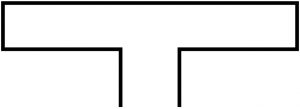
|
Folded Dipole |
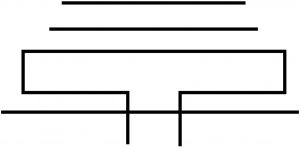
|
Folded Dipole with 2
Directors and 1 Reflector |
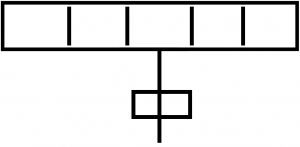
|
Slot Antenna:
Coupling RF energy into a slot in a large metallic plain can result in radiated energy with a pattern similar to a dipole antenna mounted over a reflective surface. The length of the slot is typically one-half wavelength. |
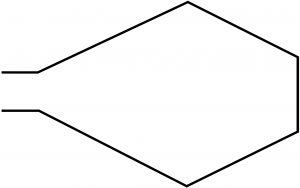
|
Rhombic Antenna:
A rhombic antenna, as its name implies, is composed of four long, straight wires arranged to form a rhombus. it is fed at one corner and terminated in a matched load at the opposite corner. Traveling waves of current. 1800 out of phase, are launched onto legs 1 and 2. |
|
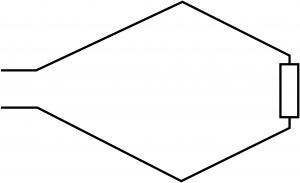
Rhombic Antenna with Resistor:
It is a normal rhombic antenna with a resistor connected between two-leg, opposite to the input fed. |

|
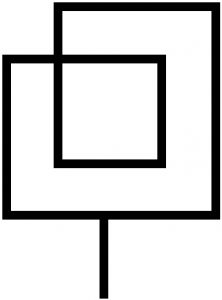
Loop Antenna |
 |
Loop Antenna (SLD) |