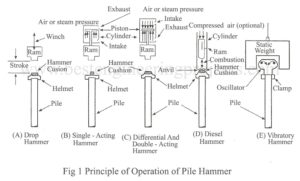
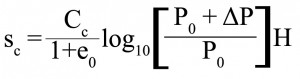Piles are driven into the ground by means of hammer. Piling Hammer are classified into following types as shown in Fig.1 Drop hammer Single acting hammer Double acting hammer Diesel hammer Vibratory hammer Drop hammer – A drop hammer is lifted up by rope and dropped freely on the pile head. During the driving operation, a cap is fixed to the top of the pile and a cushion is provided in between the pile and the cap. Single acting hammer – In a single acting hammer, a hammer is lifted…
Read MoreCategory: Civil Projects
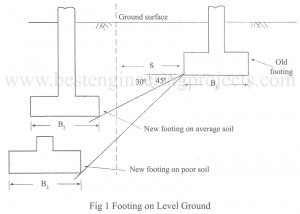
Proportional Footing for Equal Settlement
Introduction to Proportional Footing for Equal Settlement To reduce the differential settlement due to live load variations for footings on grained soils, it is desirable to proportion all the footings in such a way that they have equal pressures under the service loads. Thus all footings would settle by equal amounts and the differential settlement would be considerably reduced. Steps on proportioning footing for equal settlement as suggested by Peck et al (1974) Determine dead load of footing. Determine the footing subjected to maximum live load. Compute the ratio of…
Read MoreSpread Foundation Design Steps
What are the steps used in spread foundation design? Following are the steps used in spread foundation design. Estimate dead load, live load and other loads before spread foundation design. Estimate service load I.e. service load = DL + LL/2. Decide on depth of foundation. Assume dimension of the foundation. Find plan area. Find net load bearing capacity. Estimate allowable bearing capacity. Ensure allowable bearing capacity is equal to or greater than the loading intensity. If not revise the dimension of the footings, compute the net safe bearing capacity. Determine…
Read MoreFooting settlement of Spread Foundation
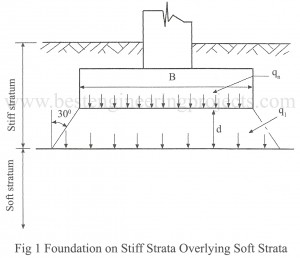
Introduction of Footing settlement of Spread Foundation The footings settlement on sands is determined from the results of plate load tests or penetration tests. The footing settlement computation from plate load tests has already been posted. The computation of footing settlement in sand from the results of penetration is not introduced in this level. (a) Foundation in non-homogeneous strata Soft Soil Overlying Firm Strata – If a foundation is to be laid on a soft strata overlying on a firm strata, the feasibility of the foundation is to be assessed. Safe…
Read MoreSecondary Settlement of Spread Foundation
What is Secondary Settlement of Spread Foundation? The secondary settlement takes place under constant effective stress. When consolidation is completed, the adsorbed water is drained out and plastic readjustments of soil particles occur. Consequently the soil mass is settled down. Secondary settlement is also negligible as compared to consolidation settlement. Settlement of Footing in Clay The total settlement is given by: Where s is the total settlement, si is the immediate settlement, sc is the consolidation settlement and ss is the secondary settlement. The secondary settlement is given by: …
Read MoreConsolidation Settlement of Spread Foundation
What is Consolidation Settlement of Spread Foundation? Consolidation settlement is caused due to the expulsion of pore water from the voids of a saturated soil mass under the prevailing excess hydrostatic pressure induced by load imposed on a foundation. Settlement of Footing in Clay The total settlement is given by: Where s is the total settlement, si is the immediate settlement, sc is the consolidation settlement and ss is the secondary settlement, The consolidation settlement is given by: = ———- (1) For normally consolidated clay, the consolidation settlement is…
Read MoreImmediate Settlement | Calculation of Immediate Settlement
Immediate settlement takes place in a short time (about a week) after the application of load and is due to elastic distortion of the soil. As the settlement is experienced in a short time, there will not be enough time for soil mass to change in its water content. Hence, Settlement takes place under constant Volume or under un-drained conditions. Immediate settlement is computed by elastic theory. Compared to consolidation settlement, particularly in saturated clay, immediate settlement is very small and often neglected unless the structure is very important. Settlement…
Read MoreAllowable Bearing Pressure
What are the allowable bearing pressure of spread foundation? Footing on Granular Soil | Allowable Bearing Pressure In cohesion less soil, the allowable bearing pressure is governed by allowable settlement. The allowable bearing pressure in sands is governed by shear failure criteria only when the footing is very narrow and below water table and the sand is loose. In sands, obtaining undisturbed sample is difficult even not impossible. Laboratory preparation of sand samples will not simulate the stress – strain relationship pertaining to situation in a representative manner. The effects of…
Read MoreDesign Load | Computation of Design Load
What are the Design Loads of Spread Foundation? Prior to the design of a foundation, the expected loads to the foundation should be assessed as accurately as possible, this loads is called design load. In general a foundation has to bear the design load. Various design load of spread foundation are described below. Dead load – This includes the weight of all permanently materials to the structure. This includes beams, floors, walls, columns and fixed service equipment. Live load – All loads which are movable from one location of the…
Read MoreFoundation Depth | Factor of Foundation Depth
What is Foundation Depth? A foundation should be provided with adequate depth so that it functions properly. The factors that govern the foundation depth are: Depth of top soil Local erosion of soil due to flowing water Underground defects such as root holes, cavities, mine shafts etc Filled unconsolidated soil Adjacent structures, property lines, excavation and future construction operation Ground water level Depth of frost penetration Depth of volume change Desiccation due to heat of boilers and furnaces Desiccation due to water drawn by roots of trees Depth of top…
Read More