What is drainage and where it is required?
Drainage is required whenever it is desirable to eliminate seepage pressure or to reduce danger from frost damage or to increase shearing resistance of soil by reducing neutral stresses. These objectives are achieved by lowering the water table below the level of a mass of soil requiring protection. When the co-efficient of permeability exceeds 0.001 cm/sec drainage is essential. When value of coefficient of permeability lies between 0.001 to 0.00001 cm/sec drainage is inconsequential but it is required for stability of sides and bottom. Drainage is not required when co-efficient of permeability is less than 10-7 cm/sec.
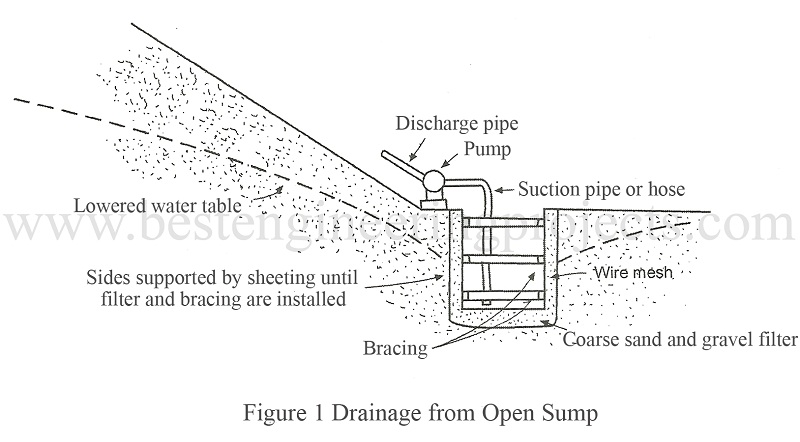
Drainage from Open Sumps
A sump is a pit with its bottom below the level an area to be drained. Drainage from open sumps method is effective when excavation depth is limited up to 2 m and soil is coarse grained. The drained water is pumped out. A filter is provided at the bottom and sides. Sheeting and bracing stabilize the sides of the ditch. This method is suitable when area to be drained is small and co-efficient of permeability exceeds 0.001 cm/sec. This is shown in Fig.1.