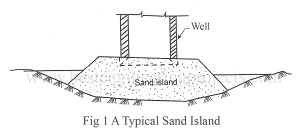
The Sinking of the Well Foundation is carried out through the following Steps. Laying of Curbs, Sinking of the Well Foundation In dry ground excavate up to 50 cm in river bed and place the cutting edge at the required position. If the curb is to be laid under water and depth of water is greater than 5 m, prepare Sand Island and lay the curb. If depth of water exceeds 5 m built curb in dry ground and float it to the site. A typical sand island is shown…
Read MoreCategory: Piers and Caissons
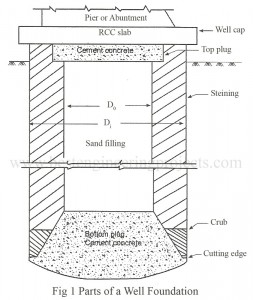
Component Parts of a Well Foundation
What are the Component Parts of a Well Foundation A section through a well foundation is shown in figure 1. The various component parts of a Well Foundation are briefly described in the following. Well Cap – The well cap is a RCC slab of sufficient strength to transmit the forces from pier to the body of well. It is generally kept at low water level. The dimension of the well cap should be sufficient to accommodate the pier. The recommended minimum thickness is 0.75 m. Steining – It is…
Read MoreCaissons | Types of Caissons | Advantage of Caissons
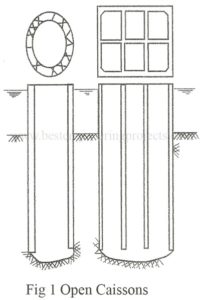
What is Caissons? The term caisson is derived from Latin, which means box or case. Caissons are hollow inside and usually constructed at site and sunk in place into a hard bearing stratum. Often the caissons have high construction cost and their construction is restricted to major foundation works. Caissons are used for bridge piers, abutments in rivers and lakes, docks and wharves, break water and other shore protections works, and large water front structures such as pump houses subjected to very heavy vertical and horizontal loads. Advantages of Caissons…
Read MoreConstruction of Pears using Mechanical Method
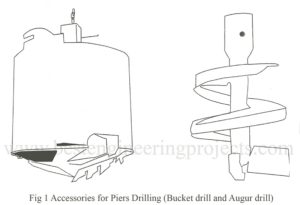
What are the Construction of pears using mechanical method Drilling – When piers are constructed by drilling, they are called drilled piers. The excavation is carried out by an auger type of drill which looks like a carpenter’s auger. The tools used are a drill bucket and a chopping bit. The drill bucket has an opening at the bottom with cutting edges or teeth. It is provided with a door to collect the cut soil. As the bucket is rotated and forced down the cutting edges save the earth and…
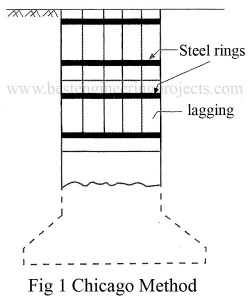
Read MoreConstruction of Piers | Manual Method
The construction of pier consists of the following operations. They include excavation, placing of the concrete and inspection after construction. The excavation is done either manually or by machines. Manual excavation is done where the site is inaccessible to machines. Manual Method | Construction of Piers The manual methods which are in common use comprise: Chicago Method Gow Method Chicago Method – Chicago method is used exclusively in clay. In this method a cylindrical hole is excavated to a depth of 0.6 m in soft clay and 1.8 m in stiff…
Read MoreBearing Capacity of Piers | Piers in Sands
Piers transfer load from soft to strata. They derive resistance from shaft and base as in the case of piles. Qult = Qb + Qs = Abqb + Asqs = ———- (1) Piers in Sands | Bearing Capacity of Piers In sands resistance in most cases is derived from base only. Shaft resistance is usually neglected due to following reasons. Depth being less than five times the width When there is possibility of scour especially in bridge foundations If there is Compressible fill If soil is liable to shrink For sand…
Read MorePiers and Caissons | Function of Pears
What are Piers and Caissons? Piers and caissons are underground cylindrical structural members that serve same purpose as footing or piles. The purpose of these structures is to transmit loads to a stratum capable of supporting it without danger of breaking of the foundation soil or excessive settlement. Usually the ratio of depth to width for piers and caissons is greater than 5. Distinction between Piers and Caissons There is no sharp distinction between piers and caissons. In simple terms caissons are large piers. They differ only in the method…
Read More