Settlement is the vertical displacement from its original level of placement. Settlement has got several implications on a foundation. The implications include:
- Appearance of structures
- Utility of structures
- Damage to the structures
Appearance of structures | Settlement of Foundation
Settlement affects the appearance of structures. If a structure settles excessively, its aesthetic is impaired. It causes doors and windows to distort, walls and plasters to crack and the structure to tilt.
Utility of Structures | Settlement of Foundation
Settlement interfere the utility of structures in many ways. If settlement is excessive overhead cranes do not operate correctly, machinery may go out of plumb and tracking units such as radar become inaccurate.
Damage to the Structure | Settlement of Foundation
If the settlement is severe, it may lead to the complete collapse of the structure even though the factor of safety against shear failure is high.
Types of Settlement | Settlement of Foundation
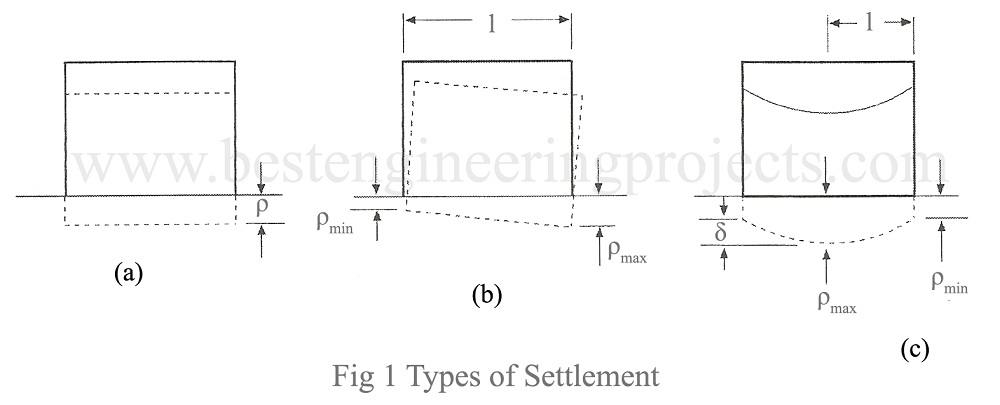
Structural rigidity, subsoil conditions and the load to be transmitted by the foundation affect settlement. On the basis of the movement of the foundation, settlement is categorized into three main types, which are shown in Figure 1. They are:
- Uniform settlement
- Tilt
- Angular distortion
Uniform Settlement – A settlement is uniform, if all pans of the structure undergo equal settlement as shown in fig.1 (a).
Uniform settlement occurs under a structure supported by a very rigid raft foundation. If the settlement is uniform, the structural failure will not take place. For example, several structures in Mexico City have suffered from very heavy settlements but they are still functioning. This is due to the settlement being uniform. However, if the uniform settlement is very excessive its function is impaired. For example, the utility services such as water supply and sewage lines, electric and telephone poles etc. may not function properly even the structure remain sound structurally.
Tilt – Tilt occurs when an entire structure rotates due to non-uniform settlement. The tilt is shown in Fig.1 (b).
Angular Distortion – When two foundations supporting columns/walls settle unequally, the structure will be subjected to angular distortion as shown in Fig.1 (c). If δ is the difference between two foundations separated by a distance L, the angular distortion is given by:
If angular distortion or tilt exceeds certain limits, the structure could fail in several ways as already mentioned.
Permissible Settlement – Different type of structures have their limit to tolerate a certain amount of maximum or differential settlement. The maximum limit of such settlement, that a structure can tolerate without impairing its structural integrity or function, is known as the permissible settlement. It is difficult to measure differential settlement and hence permissible settlement is expressed in terms of maximum total settlement. From experimental results and field observations it has been confirmed that if a structure settles to its maximum permissible value, the differential settlement is unlikely to exceed 3/4th of the maximum permissible settlement. This amount of the differential settlement is tolerable to any structure and the chances of structural damage are very minimal.