Any material will be stable at a certain slope angle. If the slope angle is greater than its safe Value, the slope will be unstable and soils/rocks located at higher elevation tend to move downwards and outwards. In such cases in order to maintain the stability of soil a retaining structure is to be provided. The soil mass behind a retaining wall, in most of the cases retains soil mass, which are vertical or nearly vertical. The purpose of the retaining structure is to maintain soils located at different locations. In the absence of a retaining wall the soil mass located at higher elevation will have a tendency to move towards the lower elevation and the soil mass will be unstable.
Like Water, every material exerts pressure to the sides and bases of a vessel in which it is contained. In water, the resulting pressure is equally transmitted in all directions of the container that it retains. In the case of the grains stored in silos or soils retained behind retaining structures, the vertical pressure exerted at the base and the lateral pressure exerted on the sides are not equal as in the case of the water. It is because of the fact that the shear strength of soil is not zero and the shear strength in soils in most of the situations will have some value.
There are three types of earth pressures. They are:-
- earth pressure at rest
- active earth pressure
- passive earth pressure.
They are elaborated in subsequent sections.
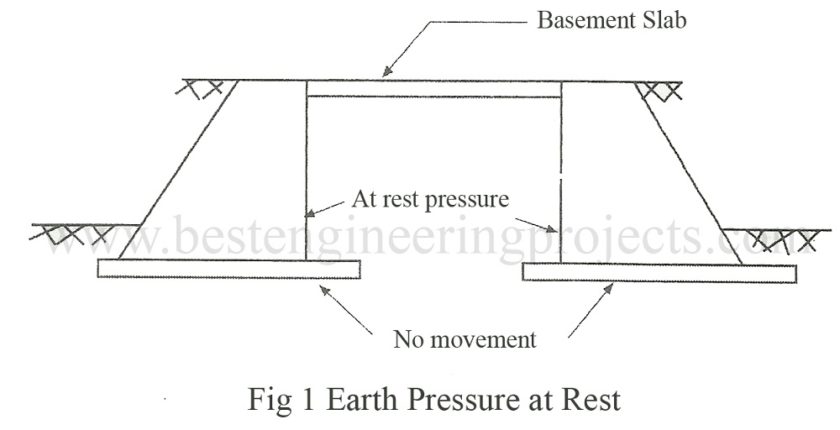
Earth Pressure at Rest
The magnitude and direction of is acting on a retaining structure and foundation depends largely upon relative strain of the soil behind the structure. When the soil is prevented from strain by an unyielding retaining structure of great rigidity, the pressure is known as the earth pressure at rest. Lateral pressure on basement wall of a building generally belongs to this category. Figure 1 shows the situation of earth pressure at rest.
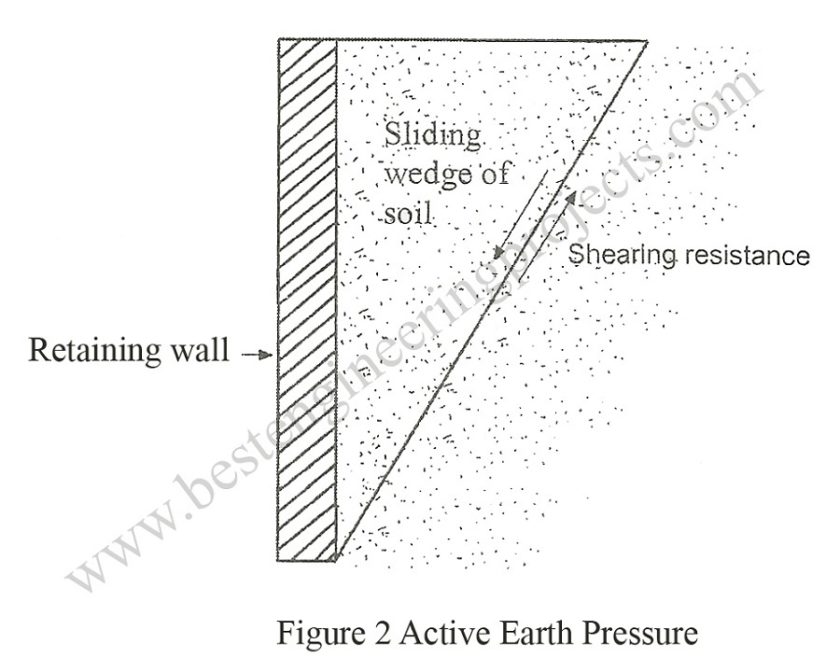
Active Type
If a retaining structure is permitted to move away from the soil allowing its lateral expansion, the pressure decreases with the increasing expansion. Further expansion will Cause a shear failure of the soil in which a sliding Wedge tends to move downward and outward. At this state of failure the pressure is at the minimum value, additional deformation doesn’t reduce the pressure any further. This minimum pressure is known as the active earth pressure. Figure 2 illustrates this situation.
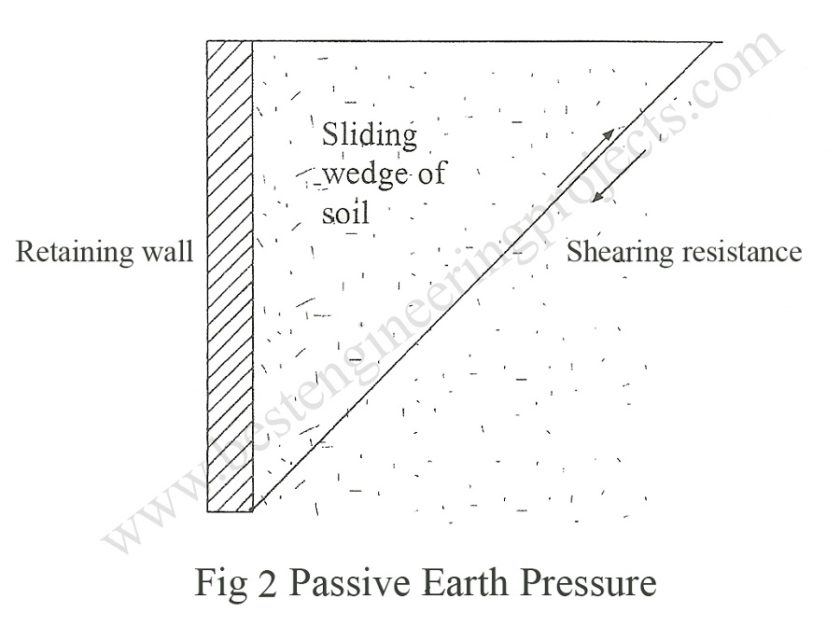
Passive Type
A state of passive pressure exists when the movement of the Wall is such that the soil is compressed horizontally. A large force is required to move the Wall to a greater distance until shear failure is reached where a sliding Wedge is formed. This wedge of soil is moved inward and upward with respect to the original position. At this stage of failure, the pressure is at a maximum value known as passive earth pressure. Figure 3 shows this situation.